Our Previous Samples
Diversity and Health Assessments NURS 6512 Week 2 Example 1Enhancing Cultural Co ...
Diversity and Health Assessments NURS 6512 Week 2 Example 1
Enhancing Cultural Competence in Health Assessment
Cultural competence is a crucial aspect of nursing practice, especially in health assessments. Functional assessments and cultural and diversity awareness play a critical role in health assessments, contributing to the delivery of effective and patient-centered care. Understanding the significance of these elements is essential for healthcare professionals, particularly nurses. Functional assessments go beyond traditional medical evaluations, focusing on a patient’s ability to perform activities of daily living (Ball et al., 2018). This includes assessing mobility, self-care, communication, and cognitive functions.
Understanding a patient’s functional status provides a holistic perspective on their health and helps identify areas requiring intervention or support. Incorporating cultural and diversity awareness ensures that healthcare providers recognize the influence of cultural, spiritual, and lifestyle factors on an individual’s health. This holistic understanding allows for more accurate health assessments that consider the whole person within their cultural context.
Issues in Health Assessments
As a nurse, I have encountered various instances where the diversity of patients has played a crucial role in healthcare delivery. It is importance to recognize and address diversity issues in health assessments. These issues encompass socioeconomic, spiritual, lifestyle, and cultural factors, emphasizing the need for personalized and culturally sensitive care.
Considering Paloma Hernandez, a 26-year-old Spanish-speaking patient, several specific factors must be taken into account. Socioeconomically, her ability to access healthcare and afford medications might be influenced. Spiritually, cultural beliefs may impact her understanding of illness and treatment (Ball et al., 2018). Lifestyle factors, including diet and daily habits, could contribute to her abdominal pain.
Building a Culturally Sensitive Health History
To develop a health history for Paloma, sensitivity to her background, lifestyle, and culture is paramount. The five targeted questions that I would ask to gather comprehensive information and assess potential health risks are:
- Cultural and Spiritual Beliefs:
Can you share any cultural or spiritual beliefs that influence how you perceive your current health condition? This may include any home remedies or traditional practices you follow.
- Diet and Lifestyle:
Could you describe your typical daily diet and any specific cultural preferences in your food choices? Additionally, are there any lifestyle factors, such as work or daily activities, that might contribute to your abdominal pain?
- Family Involvement:
In your culture, how involved is the family in health-related decisions? Do you typically rely on family members for support or assistance with healthcare matters?
- Communication Preferences:
Considering the language barrier during the first visit, I want to ensure effective communication. Is there a preferred language for our interactions, and would you like any family member, like your daughter, to be involved in translation?
- Financial Considerations:
I understand that healthcare costs can be a concern. Are there any financial challenges or constraints that may impact your ability to follow through with recommended treatments or medications?
Challenges and Strategies for Communication
Language barriers between healthcare providers and patients can impede effective communication. To overcome this, implementing professional interpreters is a crucial strategy. By ensuring accurate transmission of information, professional interpreters enable a clearer understanding of the patient’s health concerns and treatment options. This approach fosters effective communication and helps build trust between the healthcare provider and the patient.
Variations in cultural norms may lead to misunderstandings or discomfort during communication. Nurses should engage in regular cultural sensitivity training. This equips them with the skills to navigate diverse communication styles, fostering mutual understanding and trust. By being aware of and respecting cultural differences, healthcare providers can create a more inclusive and patient-centered communication environment (Dains et al., 2019).
Differences in health literacy levels impact the patient’s comprehension of medical information. To empower patients with varying health literacy levels, nurses can provide written materials in the patient’s preferred language and use visual aids. This promotes health literacy, enabling patients to actively engage in their care and make informed decisions about their health.
Family involvement expectations differ across cultures, influencing decision-making processes. Respecting and incorporating cultural norms related to family involvement in healthcare discussions is a critical strategy. This ensures holistic care planning and decision-making, recognizing the importance of family dynamics in the patient’s healthcare journey.
Strategies for Effective Cross-Cultural Communication
Nurses can prioritize culturally sensitive questions during health assessments to gather pertinent information. This approach acknowledges the influence of cultural factors on health and provides a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s background (Dains et al., 2019). By tailoring assessments to the patient’s cultural context, nurses can better address the patient’s unique healthcare needs.
Utilizing active listening techniques and employing open-ended questions are effective communication strategies. These techniques encourage patients to share their perspectives and concerns, facilitating a deeper understanding of their unique cultural context (Coleman, 2019). By actively engaging with patients and allowing them to express themselves, nurses can build trust and enhance communication.
Paying attention to non-verbal cues, including body language and facial expressions, is crucial in cross-cultural communication. Interpreting non-verbal cues enhances the nurse’s ability to gauge the patient’s comfort levels and emotional state. This contributes to a more empathetic and patient-centered interaction, bridging the gap created by language and cultural differences.
Engaging in ongoing cultural competence training and self-reflection is a continuous and essential process. Continuous learning and self-awareness foster cultural competence, enabling nurses to adapt their practices to meet the evolving needs of diverse patient populations (Coleman, 2019). By embracing cultural competence as a lifelong commitment, healthcare providers can contribute to a more inclusive and equitable healthcare environment.
Conclusion
Cultural competence is integral to providing patient-centered care, particularly in health assessments. The case study of Paloma Hernandez emphasizes the importance of understanding cultural nuances, acknowledging diversity, and employing effective communication strategies. By incorporating targeted questions and employing culturally sensitive approaches, nurses can enhance their ability to assess and address the health needs of patients from diverse backgrounds.
Diversity and Health Assessments NURS 6512 References
Ball, J. W., Dains, J. E., Flynn, J. A., Solomon, B. S., & Stewart, R. W. (2018). Seidel’s Guide to Physical Examination: An interprofessional approach. Mosby. https://www.amazon.com/Seidels-Guide-Physical-Examination-Interprofessional/dp/0323481957
Coleman, D. E. (2019). Evidence based nursing practice: The challenges of health care and cultural diversity. Journal of Hospital Librarianship, 19(4), 330–338. https://doi.org/10.1080/15323269.2019.1661734
Dains, J. E., Baumann, L. C., & Scheibel, P. (2019). Advanced Health Assessment and Clinical Diagnosis in Primary Care (6th ed.). Mosby. https://www.amazon.com/Advanced-Assessment-Clinical-Diagnosis-Primary-ebook/dp/B07M6FWXB3
Also read:
Assessment of Nutrition in Children NURS 6512
NURS 6512 Lab Assignment: Assessing the Abdomen Sample Paper
NURS 6512 Discussion: Assessing Musculoskeletal Pain Discussion Paper
NURS 6512 Assessment Tools and Diagnostic Tests in Adults and Children Case
DIVERSITY AND HEALTH ASSESSMENTS NURS 6512 WEEK 2 INSTRUCTIONS
 May 2012, Alice Randall wrote an article for The New York Times on the cultural factors that encouraged black women to maintain a weight above what is considered healthy. Randall explained—from her observations and her personal experience as a black woman—that many African-American communities and cultures consider women who are overweight to be more beautiful and desirable than women at a healthier weight. As she put it, “Many black women are fat because we want to be” (Randall, 2012).
May 2012, Alice Randall wrote an article for The New York Times on the cultural factors that encouraged black women to maintain a weight above what is considered healthy. Randall explained—from her observations and her personal experience as a black woman—that many African-American communities and cultures consider women who are overweight to be more beautiful and desirable than women at a healthier weight. As she put it, “Many black women are fat because we want to be” (Randall, 2012).
Randall’s statements sparked a great deal of controversy and debate; however, they emphasize an underlying reality in the healthcare field: different populations, cultures, and groups have diverse beliefs and practices that impact their health. Nurses and healthcare professionals should be aware of this reality and adapt their health assessment techniques and recommendations to accommodate diversity.
In this Discussion, you will consider different socioeconomic, spiritual, lifestyle, and other cultural factors that should be taken into considerations when building a health history for patients with diverse backgrounds. Your Instructor will assign a case study to you for this Discussion.
To prepare for Diversity and Health Assessments NURS 6512:
- Reflect on your experiences as a nurse and on the information provided in this week’s Learning Resources on diversity issues in health assessments.
- By Day 1 of this week, you will be assigned a case study by your Instructor. Note: Please see the “Course Announcements” section of the classroom for your case study assignment.
- Reflect on the specific socioeconomic, spiritual, lifestyle, and other cultural factors related to the health of the patient assigned to you.
- Consider how you would build a health history for the patient. What questions would you ask, and how would you frame them to be sensitive to the patient’s background, lifestyle, and culture? Develop five targeted questions you would ask the patient to build his or her health history and to assess his or her health risks.
- Think about the challenges associated with communicating with patients from a variety of specific populations. What strategies can you as a nurse employ to be sensitive to different cultural factors while gathering the pertinent information?
BY DAY 3 OF WEEK 2
Post an explanation of the specific socioeconomic, spiritual, lifestyle, and other cultural factors associated with the patient you were assigned. Explain the issues that you would need to be sensitive to when interacting with the patient, and why. Provide at least five targeted questions you would ask the patient to build his or her health history and to assess his or her health risks.
Note: For this Discussion, you are required to complete your initial post before you will be able to view and respond to your colleagues’ postings. Begin by clicking on the Reply button to complete your initial post. Remember, once you click on Post Reply, you cannot delete or edit your own posts and you cannot post anonymously. Please check your post carefully before clicking on Post Reply!
Read a selection of your colleagues’ responses.
BY DAY 6 OF WEEK 2
Respond on or before Day 6 on 2 different days to at least two of your colleagues who were assigned a different patient than you. Critique your colleague’s targeted questions, and explain how the patient might interpret these questions. Explain whether any of the questions would apply to your patient, and why.
LEARNING RESOURCES
Required Readings
- Ball, J. W., Dains, J. E., Flynn, J. A., Solomon, B. S., & Stewart, R. W. (2023). Seidel’s guide to physical examination: An interprofessional approach (10th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby.
- Chapter 1, “Cultural Competency”
This chapter highlights the importance of cultural awareness when conducting health assessments. The authors explore the impact of culture on health beliefs and practices.
- Chapter 1, “Cultural Competency”
- Dains, J. E., Baumann, L. C., & Scheibel, P. (2019). Advanced health assessment and clinical diagnosis in primary care (6th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby.
Credit Line: Advanced Health Assessment and Clinical Diagnosis in Primary Care, 6th Edition by Dains, J.E., Baumann, L. C., & Scheibel, P. Copyright 2019 by Mosby. Reprinted by permission of Mosby via the Copyright Clearance Center.- Chapter 2, “Evidenced-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines”
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, October 21). Cultural competence in health and human servicesLinks to an external site.. Retrieved from https://npin.cdc.gov/pages/cultural-competence
This website discusses cultural competence as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Understanding the difference between cultural competence, awareness, and sensitivity can be obtained on this website. - United States Department of Human & Health Services. Office of Minority Health. (n.d.). A physician’s practical guide to culturally competent careLinks to an external site.. Retrieved June 10, 2019, from https://cccm.thinkculturalhealth.hhs.gov/
From the Office of Minority Health, this website offers CME and CEU credit and equips healthcare professionals with awareness, knowledge, and skills to better treat the increasingly diverse U.S. population they serve. - Coleman, D. E. (2019). Evidence based nursing practice: The challenges of health care and cultural diversityLinks to an external site.. Journal of Hospital Librarianship, 19(4), 330–338. https://doi.org/10.1080/15323269.2019.1661734
- Young, S., & Guo, K. L. (2016). Cultural diversity trainingLinks to an external site.. The Health Care Manager, 35(2), 94–102. https://doi.org/10.1097/hcm.0000000000000100
Required Media
Module 2 Introduction
Dr. Tara Harris reviews the overall expectations for Module 2. Consider how you will manage your time as you review your media and Learning Resources for your Discussion, Case Study Lab Assignment, and your DCE Assignment (3m).
TARA HARRIS: Hello. This is Dr. Harris. I’m your coordinator for Advanced Health Assessment. Today we will discuss Module 2, which includes both week 2 and 3. During these two weeks, we will discuss functional assessments and assessment diagnostic tools. You have several required readings and articles within this module. You also have a required media video, which will assist you in learning how to take a health history.
Your first Shadow Health overview should be conducted during this time. You will also be able to complete the lab components within Shadow Health. During week 2, your discussion board initial post is due by day 3, and your final responses are due by day 6. You should also began working on your overview of Shadow Health Clinical Experience. During week 3, you have
several assignments.
Assignment 1 is a case study assignment that will be assigned by your instructor. You will need to write three to four pages within this assignment, and this does not include your title and your reference page. This assignment is due for submission by day 6 of week 3.
Your assignment 2 during week 3 will be your first Shadow Health history assessment. Please review the guidelines for this assignment. Please review your grade and rubric. Please start reviewing Shadow Health so that you are familiar with what you need to do to pass the assignment. So during week 4, this is when your health history is due. Please complete the orientation and all the requirements for this assignment.
As mentioned earlier, please review your grade and rubric. Remember, you must also document within Shadow Health as part of your grade. We are requiring that you document your information or your provider note on a Word document and submit that. Please also remember that your digital clinical score that you submit via the lab pass is not your final score. Your final grade will be composed of two components, your digital clinical score, as well as your documentation.
You must pass this assignment with a total score of 80% or more in order to pass this course. You will not be allowed any more attempts after day 7. The late policy will apply for any late submissions. Please reach out to your instructor if you need any clarity, concerns, or further discussion. Thank you.
Functional Assessments and Cultural and Diversity Awareness in Health Assessment – Week 2 (10m)
DR. LACHANDA BROWN: Hello, everyone, and welcome to Advance Health Assessment. I’m Dr. LaChanda Brown, and I’m one of the contributing faculty members in the course. For week two, we will focus on functional assessments with cultural diversity awareness. By the end of the week, you should be able to analyze diversity considerations in health assessments and apply concept theories and principles as it relates to cultural diversity in health assessment.
So what is diversity in health care and why is it so important? As a health care provider, we should be diverse, if not more diverse than the patient’s base they are treating. This helps to ensure that no matter what, no matter who walks in that door, we can effectively communicate with them and better serve their needs. We can do this be being cultural sensitive. So what is cultural sensitivity and why is it important?
Cultural sensitivity is being aware that there are cultural differences and similarities between people without assigning them a value. There’s no right or wrong, there is no better or worse, and there is no positive or negative. Again, this allows us to be able to function in other cultures, being able to understand or try to relate to being able to be that detective as previously mentioned in week one to find the correct answers, to try to solve their health problem, or help to treat their problem.
Also being culturally diverse. Cultural diversity is about appreciating that the individuals
and society are made up of different groups. That have different interests, skills, talents. It also means that being culturally diverse is being aware that there are different religious beliefs other than yourself. You may not accept those. Different sexual orientations other than yourself, but you respect that. You may not have the same belief, but you respect that, and you are non-biased for us with treatment of that patient.
So with that being said, there is always some risk of problems if there is not diversity in healthcare. And one of the issues is communication breakdown. Oftentimes, we may have individuals that may come into our practice that may have a language barrier, a different philosophy, or different cultural norms. Trying to be able to communicate, to fully communicate the needs or the issues of that patient is very important.
Also being aware of sometimes people can have lack of healthcare diversity, or you can have
limited perspectives. You may have never been around someone that may speak a different language or may have a different sexual preference or a different religious belief. And again, being able to be aware that even though this is something that you’re not familiar with, being able to try and come up with the best plan for that patient and being non-biased.
By being culturally sensitive, it provides patient-desired care, provides empowerment of the patient. The patient is aware that you are sensitive to their needs, which gives them the ability to be able to communicate and relate what is going on with them to provide better health care. I’ve also attached a video, Understanding Cultural Diversity in Healthcare- the four C’s.
Please take a look at this video. It has some very important tips on how to understand cultural diversity. So again, for this week’s assignment, you will have a case study. With that case
study, you’re going to reflect on your experience as a nurse on the information that was provided in this week’s learning resource on diversity in health issues.
Please be aware of the socioeconomic, spiritual lifestyles and other cultural factors that may be considered. Consider how you will build a health history. Again, like we discussed previously in week one, what other concepts that you need to build a good health history? What type of questions you would ask? Think about challenges, sparse with communication, and ways that you can help to relieve those communication barriers.
So again, I want to still reiterate Shadow Health assignment. Shadow health– please purchase as soon as possible. You do not have an assignment due this week for Shadow Health, but I would suggest to go ahead and practice on Shadow Health. Please get familiar with the areas in Shadow Health. If you haven’t purchased it, like I said before, you can purchase it through Walden bookstore only. You will receive an email– a confirmation
email with a code.
You do not need a PIN number from your instructor for access in Shadow Health. There is also a Shadow Health video. Just information about Shadow Health and navigation. Also attached is the Shadow Health IT. If you ever have any issues with logging in or not being able to access Shadow Health, you can click on this link and it should connect you to Shadow Health. There’s a number as well as a website to be able to contact. And then just tips for us
with Shadow Health success, starting on day one and getting familiar with Shadow Health accessing it, and just getting in the mode of Shadow Health practicing.
I cannot stress that enough. Practice, practice, practice on Shadow Health. You must have at least an 80% on Shadow Health, on all your Shadow Health, which is a combination of your DCE score as well as your documentation notes. And on those links, it will tell you about how to document. You want to be aware of the documentation that is essential. What is subjective
versus objective data? Subjective is what the patient states, what is going on with them.
Objective data is what you see or what you hear, your physical examination. So you want to
make sure that you know what is going on with your patient as far as with Shadow
Health and as far as how to document Shadow Health. Again, you must have
a 80% total combined score in Shadow Health, which is a combination of your DC score list where’s your documentation notes. And there is a link on here that can tell you how to document in your notes in Shadow Health. Again, you will start working in Shadow Health in week three.
Your first assignment is not due until week four for Shadow Health, Tina Jones. But, like I stated previously, get started with Shadow Health as soon as possible. Do not wait till
the last minute. You can practice in Shadow Health as many times as you like on up
until day seven. After day seven, you will not be able to access and it would be counted off as
late, unless you have an excuse and you previously discussed it with your instructor. But please get started on Shadow Health and get familiar. Watch the video, be aware of the IT, successful tips, and documentation tutorial. Thank you.
- Walden University. (n.d.). Instructor feedback
Diversity and Health Assessments NURS 6512 – Enhancing Cultural Competence in Health Assessment Example 2
Diversity and Health Assessment
Individuals from racial and ethnic minority groups may speak English “less well” or “not at all” and are thus classified as Limited English Proficient (LEP). Because of their limited ability to communicate their health information, ethnic minorities are vulnerable to significant health disparities. As a result, healthcare providers must be culturally competent to care for such individuals. Paloma’s case, a 26-year-old Spanish-speaking female patient who presented to the clinic for the second time in two days with abdominal pain, demonstrates the cultural influence on health. An in-depth discussion of the socioeconomic, spiritual, lifestyle, and other cultural factors influencing the patient’s health is provided below.
Socioeconomic, Spiritual, Lifestyle, and Other Cultural Factors affecting the Patient’s Health Status
An individual’s socioeconomic status influences their ability to access and use healthcare services. Poverty, health insurance, education, and employment are all important socioeconomic factors influencing Hispanic health. One in every four Hispanics in the United States lives below the poverty line (CDC, 2020). Furthermore, approximately one-third of Hispanic immigrants who have been in the United States for more than ten years had a college degree in 2018 (Noe-Bustamante, 2020). As a result, only a few people, including Paloma, have the financial means to access healthcare services.
Spiritual beliefs also influence an individual’s health status. The majority of Hispanics are Christian Catholics who seek comfort and relief from life’s stresses through prayer (Johnson & Farquharson, 2019). They believe in praying to God or having faith as a coping strategy when they are sick. This, along with seeking medical attention, may help Paloma heal. In terms of lifestyle, both Hispanic men and women report a lower prevalence of regular physical activity (41.9%, 40.5%) than their non-Hispanic counterparts (52.3, 49.6), making them vulnerable to a variety of chronic illnesses (Bantham et al., 2021).
Furthermore, in 2020, 8.0% of Hispanic adults in the United States smoked cigarettes (CDC, 2022), and it is estimated that 9.5% will have alcohol dependence at some point in their lives (National Institute of Health, 2021); these are risk behaviors that increase the individual’s risk of developing chronic illnesses. As a result, for Paloma to maintain a healthy lifestyle, she should be advised on healthy lifestyle changes. Language is a potent cultural determinant of health as well. Language influences both how a patient communicates and how a clinician perceives health information (Dains et al., 2015; Melton et al., 2014). Being an LEP, she is accompanied by her younger bilingual daughter; however, this proxy reporting of symptoms may not depict the true illness of the patient and may explain why she visits the hospital twice in two days for the same illness.
Sensitive Issues while interacting with the Patient
The patient has been to the clinic two days in a row with similar complaints. She is accompanied by her younger bilingual daughter, who may not fully comprehend all of the details of her illness. One might wonder why the patient is not with an older person, such as her husband or older children, who appear to have a better perception of health. This patient may have marital problems or some form of discord, which a clinician should be aware of to design appropriate, helpful interventions. She was also discharged on Omeprazole but was told she could get it over the counter.
Could the patient afford the medication? This could explain why she is seeking care on the second day with worsening symptoms. Poverty rates among Hispanics in the United States are staggering, with one in every four living in poverty (CDC, 2020); this may explain Paloma’s inability to afford the drugs. In addition, I would be cautious about the language I use when addressing the patient. Park et al. (2018) recommend using simple pleasantries, clear explanations, and active listening when speaking with LEP individuals to build a bond with them. While history taking is an important aspect of health assessment, the clinician must understand the patient’s situation outside of the hospital to understand the nature of the patient’s illnesses.
Targeted Questions to build the Health History and to Assess Health Risks
- You state that you have abdominal pain; when was the onset?
- In which part of the abdomen is the pain located?
- What is the character of the pain, and are there aggravating or relieving factors?
- How severe is the pain, and does it occur at different times?
- Have you ever had peptic ulcer treatment?
- Do you consume alcoholic beverages or smoke cigarettes?
- Have you recently received NSAID therapy?
- Has any member of your family ever had an abdominal malignancy?
Conclusion
History taking and physical examination are critical assessment steps in healthcare. A clinician gains essential information from the history and physical examination that aids in making a diagnosis and, consequently, designing an appropriate treatment plan. However, challenges such as language barriers may arise during the initial patient assessment, resulting in a suboptimal assessment and treatment. Paloma, for example, is Spanish-speaking and comes in the company of her bilingual-speaking younger daughter. To solve the medical problems of LEP patients, clinicians may resort to alternatives such as enlisting the assistance of a translator.
Diversity and Health Assessments NURS 6512 References
Bantham, A., Taverno Ross, S. E., Sebastião, E., & Hall, G. (2021). Overcoming barriers to physical activity in underserved populations. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 64, 64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2020.11.002
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, January 3). Hispanic health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/hispanic-health/index.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, August 9). Burden of cigarette use in the U.s. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/campaign/tips/resources/data/cigarette-smoking-in-united-states.html
Dains, J. E., Baumann, L. C., & Scheibel, P. (2019). Advanced Health Assessment & Clinical Diagnosis in Primary Care-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. https://www.uk.elsevierhealth.com/advanced-health-assessment-clinical-diagnosis-in-primary
READ MORE >>
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics AssignmentDNP 805 Week 7 Case ...
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment Details:
In this assignment, learners are required to write a case report addressing the personal knowledge and skills gained in the current course and potentially solving an identified practice problem.
CLICK HERE TO ORDER DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment General Guidelines:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment Directions:
For a specific focus of patient practice (e.g., acute care hospital, clinic, primary care, long-term care, home health), select a particular disease process DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment. Identify and fully describe the required technology elements that will be involved in providing care and define how these technologies will integrate treatment and/or monitoring from the identified care setting to the home and then to ongoing care.
Your case report must include the following:
Introduction with a problem statement
Brief literature review
Description of the case/situation/conditions
Discussion that includes a detailed explanation of the synthesized literature findings
Summary of the case
Proposed solutions
Conclusion
Portfolio Practice Hours:
It may be possible to earn Portfolio Practice hours for this case report. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
SAMPLE SOLUTION APPROACH TO THE CASE REPORT
Case Report: Health Care Informatics
DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment Introduction
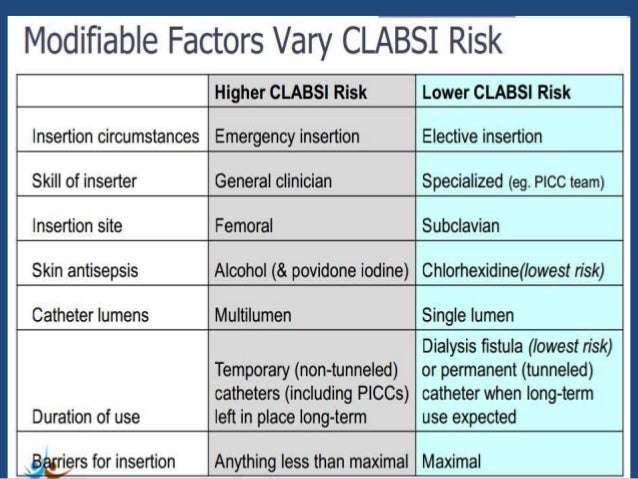
Central line associated blood stream infections (CLABSIs) continue to be a huge expense for health care organizations across the US as they cause harm to patients. Some studies have estimated that the cost of a single CLASI episode can be as much as $25,000.
Therefore, a reduction in the use of central lines in hospitalized patients can help to reduce the number of days that patients have the catheters in place and also reduce the number of CLABSIs a patient may encounter (Pathak, Gangina, Jairam & Hinton, 2018). Studies have shown that the use of care bundles that include the removal of catheters that are no longer needed is one of the most effective ways of preventing CLABSIs (Atkilla, Doganay, Celik, Tomak, Gunal, & Kilic, 2016).
However, when a central line is essential to the care of the patient, implementing measures to prevent CLABSIs is essential to prevent infections. The problem is that in the inpatient setting, nurses forget to give patients with central lines chlorhexidine baths daily as indicated per hospital protocol or they forget to documentation DNP 805 Week 7 Case Rport Health Care Informatics Assignment.
They may also forget to do the documentation of the bath even when it has been completed and leaves nurse leaders with gaps in the medical record to understand what happened when CLABSIs do occur. In this paper, the author will discuss the literature review that supports the use of chlorhexidine baths to prevent CLABSIs, discuss a case study of a patient who developed a CLABSI and describe the type of technology that is needed to help nurses take better care of patients who have a central line in place in order to prevent CLABSIs.
Applicable Care Based Technologies
Several care based technologies are possible solutions to help prevent CLABSI’s. An electronic health record (EHR) can be used to provide clinical decision prompts to allow for timely care for patients (Alexander, S., Frith, K.H., & Hoy, 2019). Computer physician order entry (CPOE) can prompt a reflex order that is generated to complete daily chlorhexidine baths whenever a physician documents or enters treatment with the insertion of a central line on a patient.
Additionally, the EHR can be designed to prompt nurses to provide chlorhexidine baths as a daily intervention that requires documentation to be completed. Clinical decision support (CDS) can be implemented in the EHR to provide alerts and reminders for patient care, provide focused data reports and summaries and provide documentation templates to help with patient care compliance (Alexander, S., Frith, K.H., & Hoy, 2019).
Integration of Technologies and Treatment/Monitoring in Care Settings
The implementation of an EHR has many possibilities for leaders in different healthcare settings that include inpatient and outpatient settings, and doctor’s offices. Records are easily accessed, data entry can be simplified, and multiple practitioners can access the records at the same time DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment.
Care can be collaborated faster and easier with an EHR than with the old paper record system and the integration of decision support technology can quickly bring the most up to date evidence based practice to the practitioner at the point of care.
Treatment and follow up can happen quickly due to the ease and accessibility of (Alexander, S., Frith, K.H., & Hoy, 2019). Therefore, with the implementation of technologies that are integrated in the EHR, a feasible solution can be found to help nurses to remember to complete chlorhexidine baths in the intensive care unit or for patients in an inpatient setting who have a central line in place.
Literature Review
In identifying a technological solution to the problem related to nurses not being compliant or consistent in giving chlorhexidine baths to prevent CLABSIs, a total of four articles were reviewed related to the use of chlorhexidine bed-baths to reduce central line associated blood stream infections (CLABSIs).
Sarani, Navidian, Jahani, Tabas & Bidar, (2017) completed a quasi-experimental study with 80 patients admitted to an ICU in a teaching hospital. Patients in the inclusion group were bathed daily with chlorhexidine 2% solution. The patients in the control group did not get a daily bath with the chlorhexidine solution.
The study revealed that 100% of the control subjects had positive culture growth after 5 days of being in the ICU without having a chlorhexidine 2% bath and identified the effectiveness of the 2% chlorhexidine solution in preventing skin colonization and skin infections in ICU patients. In a second study, Cleves, Pino, Patino, Rosso, Velez & Perez (2018) demonstrated a significant reduction in CLABSI rates in neonates with the use of chlorhexidine baths.
A reduction from 8.64 to 4.28 was seen CLABSIs per 1000 was observed in the unit. A third study by Reagan et al., (2019), showed that an increase in chlorhexidine bathing compliance from 60% to 90% prevented 20 infections and saved almost one million dollars in costs for patient care DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment.
As bathing compliance increased, the study showed that the overall costs of infections subsequently decreased. Kim, Lee, Na, Roh, Shin & Kim (2016) completed a meta-analysis with eighteen studies that concluded that there was a greater reduction for CLASISs among critically ill patients with chlorhexidine bathing. The study found that the risk for CLABIs is reduced when chlorhexidine baths are completed daily.
Description of Case
On day 1, Patient Clark (PC), a 67 year old female, was admitted to the cardiovascular intensive care unit (ICU) with an acute myocardial infarction. On day 2, a central line was placed and she was taken to the cardiac catheterization lab. On day 4, the central line was still in place.
PC became confused and she was having chills and her temperature was 38.4 degrees Celsius. She went from a sinus rhythm on the cardiac monitor to a sinus tachycardia and her blood pressure dropped from 120 systolic to 92 systolic. An infection was suspected and the physician ordered blood cultures to be drawn. On day 5, the culture was resulted and identified enterococcus faecalis as the organism in the blood. Since the central line was in place for greater than 2 calendar days on the date of the fever and there was no other identified site of infection, PC was diagnosed with a central line associated bloodstream infection. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
A review of the chart indicated that the nurses had not documented a chlorhexidine bath on days 2, 3 or 4 of her stay in the intensive care unit. Although a daily chlorhexidine bath was a unit based protocol for infection prevention in the critical care unit, the nurses had not consistently ensured or documented that she had received the bath. The infection control nurse and nurse educator of the intensive care unit reviewed potential root causes of the CLABSI and identified the lack of completion of daily chlorhexidine baths as contributing to the CLABSI. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
Synthesized Literature findings
The literature review identified the need for consistent daily baths with chlorhexidine to prevent the development of a CLABSI in patients who have a central line or for patients admitted to an intensive care unit (Sarani, Navidian, Jahani, Tabas & Bidar, 2017). Additionally, Reagan et al. (2019) identified that an increase in chlorhexidine bathing compliance would reduce the number of infections and thus prevent CLABSIs.
Proposed Solution
The proposed solution is to include a tool in the electronic health record (EHR) that allows nurses a location to document the completion of a chlorhexidine bath. The CPOE would include a reflex order for nurses to ensure the completion of a daily chlorhexidine bath whenever a physician enters a central line as an intervention or whenever the nurse documents the presence of a central line daily. CDS would allow for data tracking that allows daily reports to be run and shared with nurse leaders to indicate compliance of documentation.
Nurse leaders would then be able to track and trend data and monitor for compliance with the chlorhexidine bathing protocol for the patient care area and share the information with stakeholders as indicated. Additionally, the most important part of the solution is to implement an alert system in the EHR that notifies a nurse when a patient is 2 hours away from the 24-hour mark of their last chlorhexidine bath. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
When the patient is at the 24-hour mark of their last chlorhexidine bath, there would be a second alert. The purpose of the first alert is to allow the nurse time to evaluate the plan of care and facilitate having the patient receive a chlorhexidine bath within the remaining two-hour window. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
The second alert is a reminder that would pop up only if the nurse had not yet documented the bath being completed after the first alert was triggered. Therefore, this alert system would give the nurse two reminders to ensure compliance with the chlorhexidine bath is achieved. The alert system would close the technology gap and serve as a reminder for the nurse to provide timely evidence-based care.
Conclusion on DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
Care based technology has revolutionized the way care is being delivered to patients in multiple healthcare settings. The use of EHRs, CPOE, CDS systems and data mining tools are all forms of technology that can provide feasible solutions to many identified patient care problems identified in healthcare.
The research has shown that the daily intervention of a chlorhexidine bath for critical care patients and those with a central line can help to reduce or prevent a central line associated blood stream infection. Using the available technology, a system can be built that serves as a reminder for nurses to complete tasks such as giving chlorhexidine baths to patients in this population.
References on DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
Alexander, S., Frith, K.H., & Hoy. (2019). Applied clinical informatics for nurses. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Atilla, A., Do?anay, Z., Çelik, H. K., Tomak, L., Günal, Ö., & K?l?ç, S. S. (2016). Central line-associated bloodstream infections in the intensive care unit: importance of the care bundle. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology, 69(6), 599–603. https://doi-org.lopes.idm.oclc.org/10.4097/kjae.2016.69.6.599
Cleves, D., Pino, J., Patiño, J. A., Rosso, F., Vélez, J. D., & Pérez, P. (2018). Effect of chlorhexidine baths on central-line-associated bloodstream infections in a neonatal intensive care unit in a developing country. Journal of Hospital Infection, 100(3), e196–e199. https://doi-org.lopes.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2018.03.022
Kim, H. Y., Lee, W. K., Na, S., Roh, Y. H., Shin, C. S., & Kim, J. (2016). The effects of chlorhexidine gluconate bathing on health care–associated infection in intensive care units: A meta-analysis. Journal of Critical Care, 32, 126–137. https://doi-org.lopes.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.11.011
Pathak, R., Gangina, S., Jairam, F., & Hinton, K. (2018). A vascular access and midlines program can decrease hospital-acquired central line-associated bloodstream infections and cost to a community-based hospital. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 1453. https://doi-org.lopes.idm.oclc.org/10.2147/TCRM.S171748
Reagan, K. A., Chan, D. M., Vanhoozer, G., Stevens, M. P., Doll, M., Godbout, E. J., Cooper, K., Pryor, R. J., Hemphill, R. R., & Bearman, G. (2019). You get back what you give: Decreased hospital infections with improvement in CHG bathing, a mathematical modeling and cost analysis. American Journal of Infection Control, 47(12), 1471.
Sarani, H., Navidian, A., Jahani, S., Tabas, E. E., & Bidar, S. (2017). Evaluation of the Daily Chlorhexidine Bath Effect on Skin Colonization of the Intensive Care Unit Patients. Medical-Surgical Nursing Journal, 5(4), 38–44. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
I, (John Doe), verify that I have completed (10) clock hours in association with the goals and objectives for this assignment. I have also tracked said practice immersion hours in the Typhon Student Tracking System for verification purposes and will be sure that all approvals are in place from my faculty and practice mentor.
DNP 805 Week 8 Assignment Evaluation of Health Care Technology
For this assignment, you will utilize content from the course materials as well as additional qualified resources to synthesize new information which you can apply towards your DPI Project, your future work area or your clinical practice as a DNP-prepared nurse.
General Guidelines:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
- You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
Directions:
For this assignment, write a 1,000-1,250 word paper in which you:
- Select a technology that has been explored in the course.
- Perform an assessment using elements of user-technology interface or human factors methods to determine functionality.
- Using the content in the readings and textbook, list three elements that will be used to evaluate the user-technology interface.
- Select a technology and list the elements that will be evaluated. Include their definition and describe how the element would be measured or evaluated.
- For each element, propose practicable suggestions for improvement using support from the literature.
Portfolio Practice Hours
It may be possible to earn Portfolio Practice hours for this case report. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
CLICK HERE TO ORDER DNP 805 SOLUTIONS
DNP 805 Week 8 Assignment Reflective Journal
Details:
Learners are required to maintain a reflective journal integrating leadership and inquiry into current practice.
In your journal, reflect on the personal knowledge and skills gained in the this course and address a variable combination of the following: new practice approaches, intraprofessional collaboration, health care delivery and clinical systems, ethical considerations in health care, population health concerns, the role of technology in improving health care outcomes, health policy, leadership and economic models, and/or health disparities.
Outline what you have discovered about your professional practice, personal strengths and weaknesses that surfaced, what additional resources and abilities could be introduced to a given situation to influence optimal outcomes, and finally how you met the competencies aligned to this course. DNP 805 Week 7 Case Report Health Care Informatics Assignment
You are not required to submit this assignment to Turnitin.
Submit your reflective journal both to the instructor and in the Typhon Tracking System under the corresponding course section. Failure to submit your journal in both the course room and Typhon systems may result in a grade of Incomplete for the course. Course Tutor Source Therapeutic communication is central to baccalaureate nursing practice.
READ MORE >>
DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology AssignmentDNP 805 Week 8 Eva ...
DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment
DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment Details
For this assignment, you will utilize content from the course materials as well as additional qualified resources to synthesize new information which you can apply towards your DPI Project, your future work area or your clinical practice as a DNP-prepared nurse.
CLICK HERE TO ORDER DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment
Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment General Guidelines:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
- You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment Directions:
For this assignment, write a 1,000-1,250 word paper in which you:
- Select a technology that has been explored in the course.
- Perform an assessment using elements of user-technology interface or human factors methods to determine functionality.
- Using the content in the readings and textbook, list three elements that will be used to evaluate the user-technology interface.
- Select a technology and list the elements that will be evaluated. Include their definition and describe how the element would be measured or evaluated.
- For each element, propose practicable suggestions for improvement using support from the literature.
Portfolio Practice Hours
It may be possible to earn Portfolio Practice hours for this case report. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
SAMPLE SOLUTION APPROACH FOR WEEK 8 TASK
DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment Specific Technology Explored
Healthcare Information Technology (HIT) is transforming how the healthcare system functions. A major component that have emerged among HIT to expand the quality and effectiveness of healthcare and enhance health inequalities is the Electronic Health Records (EHRs). Currently, EHRs are one of the most prevalent technologies and have been successfully implemented in most healthcare systems in the United States (U.S.) (Kruse, Stein, Thomas & Kaur, 2018).
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH Act) was recognized into law in 2009 and to reinforce Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), HITECH has established incentives for hospitals and providers that implement EHR technology. In order to receive the incentives, organizations must employ qualified EHR technology that provides electronic health information to improve patient care quality. The goal in implementing any healthcare technology is to increase transparency, improve collaboration between providers and facilities, and exchange and store patient information confidentially and securely (Nagle, Sermeus & Junger, 2017).
Assessment of User-Technology Interface or Human Factors Methods
HIT implementation does not warrant enhancements in the patient quality of care or patient safety. Researchers have linked the lack of success to lack of human factors and ergonomics (HFE) or Human Factors Engineering. The importance of HFE methods are one of the important topics that is relevant in the patient safety considerations in the proposal and implementation of HIT. The focal point of HFE is on perfecting human performance by considering their belief and physical weaknesses (Carayon & Hoonakker, 2019).
Studies have confirmed that crucial applications of HFE in the early stage of any technology design implementation can be advantageous for both clinicians and patients. HFE and usage methods are be embedded as fundamental elements of HIT promotion, application and impact evaluation. EHR systems implementation need to adhere to the same design regardless of the specific product.
Even a slight software upgrade will significantly impact clinicians if the user interface is altered. It is perhaps astonishing that, as these systems become more universal, there has been a rise in accounts of HFE and usage difficulties with EHR systems globally. The American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA), has endorsed an HFE and usability research program to focus on consistency for EHR functionalities, develop measures for adverse events associated to health IT use and promote best evidenced-base practices for safe implementation of EHRs (Turner, Kushniruk & Nohr, 2017).
In the early stages of EHRs, many organizations have thought that the relocation of records and systems implementation would be a one-time project. There will always be time when organizations will need to switch to new systems and sellers for specific EHR equipment, as well as home-based software built to concentrate on organization’s specific wants.
Given the growing complexity of medical care with multiple systems and providers, information technology (IT) can gather detailed medical data to provide effective care and improve health decision-making. Human dynamics problems are to be considered in the proposal and incorporation of healthcare technology system delivery to enhance quality of care (Patel & Kannampallil, 2014).
Three Elements EHR Technology to Evaluate User-Technology Interface
EHR systems are considered a critical factor in the transformation of the healthcare industry. The capability to provide high quality healthcare is closely entwined to the quality of an EHR’s user interface plan. Simply stated, a poor EHR design can cause user errors that can be harmful to the patient injury and cause even death.
EHR’s function in patient care is developing significantly as health information interactions are implemented and new methods to complement efficiency are grouped and made available for decision support. Evaluating EHR methodically after implementation is indispensable, guiding principle for standardization are required to promote enhanced evidenced-based research plan to expand the success and efficiency of EHRs, and thus decrease the occasion for patient harm from user mistakes and errors. Elements of the EHR technology to Evaluate User-Technology Interface can be categorized in three steps. 1) The Application Analysis, (2) the User Interface Expert Evaluation, and lastly (3) User Interface Validation Examination (National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 2015).
Definition/description of Each Element of Specified Technology
The first element Application Analysis is both a key factor of user-centered expansion and the basis for all succeeding analysis and testing activities. The Application Analysis deeply depend on the EHR application designer’s user wants and system requirements analysis. In this step an explanation should be provided on the design of the application’s user interface, the identification of the system’s expected operators, descriptions of the usage settings and how the design will be adjusted. The analysis should be operated by a multidisciplinary team incorporating the application developer team, clinical specialists and human factors providers and those delivering direct application knowledge (NIST, 2015).
The second element is EHR User Interface Expert Review in this step the Expert Review is directed by a mixture of the vendor’s developer team and devoted team of medical safety and usability experts. The assessors match up the EHR’s user interface project to scientific design ideologies and ethics and detect any design problems that can lead to safety threats. Succeeding to this review, the application designer may elect to adjust parts of the application’s user interface to eradicate issues or departures from recognized best practice that can cause patient safety risks (NIST, 2015).
The third element is EHR User Interface Validation Test in this step evaluation of the actual user execution related to patient safety found in the earlier steps is done, as well as a validation test is led by skilled usability/human factors specialists before the implementation of EHR system. Performance is scrutinized by gathering user performance information that are pertinent pointers of the existence of safety issues. These actions may incorporate goal for effective task achievement, assessment of quantity of errors and revised errors, performance complications and failures to achieve task effectively or in appropriate classification.
Performance is also assessed by conducting post-test discussions that focus on what the users have identified as risks due to confusion when completed scenarios that was developed by the test teams who will and adjust the examples as needed for their medical situation. The purpose of the validation test is to ensure that patient safety is not affecting by vital interface design problems related to use error (NIST, 2015).
Proposal That Provide Practicable Suggestions for Improvement
EHRs present great promise for refining and transforming the healthcare developments and outcomes, as well as enhancing patient safety. This will work only if HER systems are correctly constructed and data are used accurately. EHR vendors, lawmakers and healthcare providers must all collaborate to make sure that EHR systems lead to improved patient care instead of causing medical mistakes.
The complications, defects and other unintentional effects with EHR design and use that impede patient safety must be addressed in order to attain superior quality of care. National guidelines should be decreed that establish EHR system criteria and implementation requirements.
These rules should be established for both sellers and users of EHR systems concerning the proper use of documentation practices to guarantee comprehensive, truthful and outstanding documentation. Healthcare organizations should make sure that all workers have in-depth training on EHR system use, as well as creating a working atmosphere that encourage reliable practices and the establishment must also make sure that the system is fitting for the clinical missions for which it is being use.
As previously stated, EHR can change the way healthcare is provided when it is planned, executed, and utilized correctly, otherwise it can add various complication to the already multifaceted healthcare delivery, leading to unintentional outcomes for instance medications errors, failure to identify severe diseases, delays in treatment, increase healthcare costs (Graber, Byrne & Johnston, 2017).
References on DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment
Carayon, P., & Hoonakker, P. (2019). Human Factors and Usability for Health Information Technology: Old and New Challenges. Yearbook of medical informatics, 28(1), 71–77. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1677907.
Graber, M. L., Byrne, C., & Johnston, D. (2017). The impact of electronic health records on diagnosis. Diagnosis (Berl), 4(4), 211–223. doi: 10.1515/dx-2017-0012.
Kruse, C. S., Stein, A., Thomas, H., & Kaur, H. (2018). The use of Electronic Health Records to Support Population Health: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Journal of medicalsystems, 42(11), 214. doi:10.1007/s10916-018-1075-6.
Nagle, L. M., Sermeus, W., & Junger, A. (2017). Evolving role of the nursing informatics specialist. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 232, 212.
National Institute of Standards and Technology. (2015). Technical Evaluation, Testing, and Validation of the Usability of Electronic Health Records. Retrieved from:
https://www.nist.gov/system/files/documents/2017/04/28/EUP_WERB_Version_2_23_12-Final-2.pdf.
Patel, V. L., & Kannampallil, T. G. (2014). Human factors and health information technology: current challenges and future directions. Yearbook of medical informatics, 9(1),8-66.
Turner, P., Kushniruk, A., & Nohr, C. (2017). Are We There Yet? Human Factors Knowledge and Health Information Technology – the Challenges of Implementation and Impact. Yearbook of medical informatics, 26(1), 84–91. doi:10.15265/IY-2017-014.
Practice Immersion Hours Completion Statement DNP-805
I, (Jane Doe), verify that I have completed (20) clock hours in association with the goals and objectives for this assignment. I have also tracked said practice immersion hours in the Typhon Student Tracking System for verification purposes and will be sure that all approvals are in place from my faculty and practice mentor.
DNP 805 Week 8 Assignment Reflective Journal
DNP 805 Week 8 Evaluation of Health Care Technology Assignment Details:
Learners are required to maintain a reflective journal integrating leadership and inquiry into current practice.
In your journal, reflect on the personal knowledge and skills gained in the this course and address a variable combination of the following: new practice approaches, intraprofessional collaboration, health care delivery and clinical systems, ethical considerations in health care, population health concerns, the role of technology in improving health care outcomes, health policy, leadership and economic models, and/or health disparities. Outline what you have discovered about your professional practice, personal strengths and weaknesses that surfaced, what additional resources and abilities could be introduced to a given situation to influence optimal outcomes, and finally how you met the competencies aligned to this course.
You are not required to submit this assignment to Turnitin.
Submit your reflective journal both to the instructor and in the Typhon Tracking System under the corresponding course section. Failure to submit your journal in both the course room and Typhon systems may result in a grade of Incomplete for the course.
READ MORE >>
simulated cases are not acceptable for practice immersion hours and therefore n ...
READ MORE >>
or as a complex inheritance and considerations for practice and patient educati ...
READ MORE >>
DNP 810 Course Papers – Emerging Areas of Human Health GCU NewDNP 810 Course P ...
DNP 810 Course Papers – Emerging Areas of Human Health GCU New
DNP 810 Course Papers
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAYS, INSTRUCTION-COMPLIANT PAPER – DNP 810 Course Papers
Health Issues for the Aging Essay Example
Aging cause major socio-economic effect for the community, including the healthcare organizations. As people ages, their health generally declines requiring more medical attention. They are also at higher risk for chronic disease such as: Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, arthritis, heart disease and particularly falls which can impact their health and quality of life (Awang, Mansor, Nai Peng & Nik Osman, 2018). Falls are the major reason of injury in adults aged 65 years or older.
Falls often generate moderate to severe harms like head trauma, fractures and death leading to longer hospital stays, unnecessary admissions/readmissions and increase the healthcare expenditures (Jin, 2018) DNP 810 Course Papers. Given the aging population growth and the damaging effect of falls, this paper will analyze how to incorporate quality improvement solutions into public policy in order to reduce the occurrence of falls and fall-related damage in the aging population.
Evaluation of Literature, Suggestions, Resolution to Issue
Fall is a major public health issue that can bring about serious injuries and even death in the elderly. In 2014, approximately 27,000 elderly died from unintentional fall injuries and the emergency departments treated 2.8 million elderly of which 742,000 required hospitalization. Elderly fall cost approximately $35 billion in 2012 and is expected to increase to $100 billion in 2030, without the cost for therapy and grievances.
Falls created over 20 million dollars annually and increased hospital stay to an extra 6.9 days costing the patient an extra $13,806 (Phelan, Mahoney, Voit & Stevens, 2015). Since falls can be prevented, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services since 2008 have stopped reimbursing hospitals for detrimental fall-related injuries DNP 810 Course Papers. As a result, fall prevention have become for the healthcare systems both a financial and patient safety importance.
Healthcare organizations have put into effect various programs to prevent falls among patients. Preventing falls is important to preserve patient safety and decrease the financial weight on the healthcare system (Staggs, Mion & Shorr, 2015). Decreasing and preventing falls among the elderly has been a focus of study for years due to the rising number of individuals living into older age.
Many interventions such as exercise, home safety assessment, modification and multifactorial have been established through randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and subsequently condensed in systematic reviews and meta-analyses and have been showed to be effective in preventing falls among the elderly (Stubbs, Brefka & Denkinger, 2015) DNP 810 Course Papers.
Solutions and development of approaches to decrease the incidence of falls have been a noticeable emphasis in the literature for years DNP 810 Course Papers. There is now convincing indication that falls can be averted with a variety of resolutions. Studies have shown that exercise programs and home/environment evaluations by an occupational therapist can reduce the number of falls (Pighills, Ballinger, Pickering, & Chari, 2016)
Incorporating Solution into Public Policy
The United States (US) population is aging, quickly, the number of older adults is anticipated to increase from 50 million to 75 million as the last group of baby boomers turns 65. By 2034, older adults are predicted to be more than their children in the nation’s history (Naylor, Hirschman, Hanlon, Bowles, Bradway, McCauley, & Pauly, 2014).
The urgency to incorporate falls prevention among older adults into public policy should be considered. Policy, research and practice are unified elements needed for a successful and workable program of falls prevention for the elderly DNP 810 Course Papers. The development and complicated nature of fall risk among a fast-growing aging populace requires a practical and organized approach to prevention.
The function of policy is to grant the infrastructure and funding necessary for the incorporation of falls prevention into practice. Research is essential to provide facts to support the successful application of fall prevention interventions DNP 810 Course Papers. Practice is where evidence is employed based on the guidelines and rules set by policy (Houry, Florence, Baldwin, Stevens & McClure, 2016).
Medicaid and Medicare which is the second and third major health insurance providers in the US has several policies that can be used to tackle falls prevention, however, they have not all been used to their full benefits. As the guarantor of more than 48 million Americans elderly, the Medicare program can demand, authorize, and incentivize provider actions associated to falls prevention.
Additionally, numerous Medicare Advantage (MA) plans have contracted with community-based establishments to offer falls prevention services to the elderly consisting of free fitness programs and Silver-Sneakers programs (Horton, Dwyer & Seiler, 2018) DNP 810 Course Papers.
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAYS, INSTRUCTION-COMPLIANT PAPER – DNP 810 Course Papers
Determining Barriers to Implementation of Solution
Implementation of falls prevention can be guided by several reasons including environmental and circumstantial problems; staff understanding, views and mindsets; organizational values and climate; staff assignments; and access to correct equipment and funds DNP 810 Course Papers.
Barriers can include viewpoints that falls cannot be avoided, inadequate understanding on falls prevention in patients with multifaceted care needs like cognitive impairment, lack of funds and involvement in falls prevention efforts (Ayton, Barker, Morello, Brand, Talevski, Landgren, Melhem, Bian, Brauer, Hill, Livingston & Botti, 2017).
Managing falls in the elderly can be difficult due to their multi-factorial make-up. Contributing factors include environmental/home hazards, poor health and functional debilities. Despite various successful interventions to prevent falls among the elderly, such as multi-component exercises, home hazard adjustments, medication evaluations, healthcare providers may not be prepared to manage falls due to numerous challenges.
Both elderly and clinicians need to adjust their traditional ways of living and working in order to adopt new approaches and actions that can decrease falls (Loganathan, Ng, Tan & Low, 2015). Other barriers in implementing fall prevention solutions is a lack of organization between diverse local, state and federal organizations DNP 810 Course Papers.
Even though various agencies have their own falls prevention plans, there is no main agency that organizes programs/actions being managed by all of them. In addition, funds offered to the states often must undergo diverse regulations and restrictions DNP 810 Course Papers. At the state level, fall/injury prevention programs particularly tend have a low importance, and normally there is only one person organizing state-wide efforts (Healthy housing solutions, 2017).
Options for Public and/or Private Funding
Many states have allocated funds to create and uphold statewide fall prevention plans. For instance, the Massachusetts government have launched a fall prevention plan, which propose prevention stratagems in a yearly report DNP 810 Course Papers. Washington also have an established fall prevention program and funding for services provided by the program.
In 2008, Congress approved the Safety of Seniors Act, which orders the secretary of health and human services to give funding and to support states that have various elderly fall prevention programs. The states of Minnesota, Kentucky, New Hampshire and California have utilized the ‘Core Injury Prevention” Grants funding from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s “National Center for Injury Prevention and Control” to form local teams that support evidence-based plans for fall prevention (Scotti, 2016).
The Administration on Aging, a program within Administration for Community Living (ACL), has given over $4.8 million grants for the development and implementation evidence-based falls prevention services and tactics nationwide DNP 810 Course Papers. ACL awarded ten grants to public and private not-for-profit units, as well as state organizations and community, and four grants to ethnic organizations (ACL, 2019). Policymakers need to allocate adequate funding for the development of effective falls prevention plans.
The CDC through the “Center for Injury Prevention”, participates in a variety of surveillance, study, and activities implementation to decrease elderly falls DNP 810 Course Papers. The CDC appraises data to find and broadcast valuable falls prevention programs, develops teaching tools for providers and sustains state attempts to decrease elderly falls through the “Core State Violence and Injury Prevention Program” funding.
The government’s FY2018 budget have planned to remove funding for falls prevention programs at the CDC, however, the Senate has instead advised to continue financing the CDC’s fall programs at around $2 million a vital ongoing savings that would increase in future years considering the fifty billion in yearly medical expenses to manage falls (Horton, Dwyer & Seiler, 2018).
Recommended Solution
When taking measures to apply recommended solution for falls, the reasons that generate fall must be considered for instance intrinsic and extrinsic risk. Intrinsic risk can be attributed to normal aging process and acute or chronic medical issues. Extrinsic factors are associated to the physical environment for example unsuitable floor conditions, lack of grab bars, defective or inappropriate use of equipment (Frieson, Tan, Ory & Smith, 2018).
The CDC has founded a process termed “STEADI” (Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths, and Injuries) that provides guided interventions to help clinicians integrate falls assessment and prevention into their establishment DNP 810 Course Papers. Also implementing the American Geriatrics Society’s guideline will help providers to decrease elderly falls. Another way to reduce fall is through continuing education trainings for providers to better assess the elderly at risk of falls through appropriate management and referral to fall prevention programs.
Clinicians also need to provide home adjustments help support to keep the elderly safe in their homes to reduce and prevent falls. Lastly, incorporating medication review is important in assessing elderly at fall-risk DNP 810 Course Papers. Several groups of medications, principally psychoactive, antidepressants and sedatives medication put the elderly at greater risk, they are provable predictors of falls as they alter the sensorium and destabilize gait and balance (Casey, Parker, Winkler, Liu, Lambert, & Eckstrom, 2017).
To conclude, the inevitable growth in elderly people produce several age-related chronic diseases and severe problems on quality of life. It is important for DNP-prepared nurses to quickly detect those at risk for fall and increase the community awareness of falls prevention. Given the injurious effects falls have on patients and the high cost on the patient and the healthcare system, there is need for clinicians to promote preventive care and make sure to perform methodical assessment as well as a thorough physical examination, fall assessment, medication review, functional and environmental assessment (Khadka & Darai, 2018).
With each preventing falls, the patients/families, providers and the healthcare organizations all profit. DNP-prepared nurses have an integral responsibility in decreasing fall among the elderly DNP 810 Course Papers. Understanding older adults’ standpoint on falls prevention and how to get them involve in fall prevention activities is important to keep the elderly safe in their homes and communities rather than going to nursing home care (Phelan, Mahoney, Voit & Stevens, 2015).
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAYS, INSTRUCTION-COMPLIANT PAPER – DNP 810 Course Papers
DNP 810 Course Papers References
- Administration for Community Living (ACL). (2019). ACL Funds Evidence-Based Falls Prevention Grants. Retrieved from https://acl.gov/news-and-events/announcements-latest-news/acl-funds-evidence-based-falls-prevention-grants.
- Awang, H., Mansor, N., Nai Peng, T., & Nik Osman, N. A. (2018). Understanding ageing: fear of chronic diseases later in life. The Journal of international medical research, 46(1), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060517710857.
- Ayton, D. R., Barker, A. L., Morello, R. T., Brand, C. A., Talevski, J., Landgren, F. S., Melhem, M., Bian, E., Brauer, S. G., Hill, K. D., Livingston, P. M., & Botti, M. (2017). Barriers and enablers to the implementation of the 6-PACK falls prevention program: A pre-implementation study in hospitals participating in a cluster randomised controlled trial. PloS one, 12(2), e0171932. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171932.
- Casey, C. M., Parker, E. M., Winkler, G., Liu, X., Lambert, G. H., & Eckstrom, E. (2017). Lessons Learned From Implementing CDC’s STEADI Falls Prevention Algorithm in Primary Care. The Gerontologist, 57(4), 787–796. doi:10.1093/geront/gnw074.
- Frieson, C. W., Tan, M. P., Ory, M. G., & Smith, M. L. (2018). Editorial: Evidence-Based Practices to Reduce Falls and Fall-Related Injuries Among Older Adults. Frontiers in public health, 6, 222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00222.
- Horton, K., Dwyer, G., & Seiler, N. (2018). Older Adult Falls—Costly But Not Inevitable. Retrieved from https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/hblog20180402.25780/full/.
- Houry, D., Florence, C., Baldwin, G., Stevens, J., & McClure, R. (2016). The CDC Injury Centers Response to the Growing Public Health Problem of Falls Among Older Adults. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, 10, 74-77.
- Jin, J. (2018). Prevention of Falls in Older Adults. JAMA, 319(16),1734.
- Khadka, A., & Darai, A. (2018). Common Health Problems and their contributing factors among elderly residing in Changu VDC. Journal of Institute of Medicine, 40(1), 103–107.
- Loganathan, A., Ng, C. J., Tan, M. P., & Low, W. Y. (2015). Barriers faced by healthcare professionals when managing falls in older people in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: a qualitative study. BMJ, 5, e008460.
- Naylor, M. D., Hirschman, K. B.,. Hanlon, A. L ., Bowles, K. H., Bradway, C., McCauley, M., & Pauly, M. V. (2014). Comparison of evidence-based interventions on outcomes of hospitalized, cognitively impaired older adults. Journal of Comparative Effectiveness Research, 3(3), 245-257.
- Phelan, E. A., Mahoney, J. E., Voit, J. C., & Stevens, J. A. (2015). Assessment and management of fall risk in primary care settings. The Medical clinics of North America, 99(2), 281–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2014.11.004.
- Pighills, A., Ballinger, C., Pickering, R., & Chari, S. (2016). A critical review of the effectiveness of environmental assessment and modification in the prevention of falls amongst community dwelling older people. British Journal of Occupational Therapy, 79(3), 133-143.
- Scotti, S. (2016). Preventing Elderly Falls. National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL), 24, 17.
- Staggs, V. S., Mion, L. C., & Shorr, R. I. (2015). Consistent differences in medical unit fall rates: Implications for research and practice. Journal of American Geriatric Society, 63(5), 983987.
- Stubbs, B., Brefka, S., & Denkinger, M.D. (2015). What works to prevent falls in community- dwelling older adults? Umbrella review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther, 95, 1095–1110.
- Casey, C. M., Parker, E. M., Winkler, G., Liu, X., Lambert, G. H., & Eckstrom, E. (2017).
Lessons Learned From Implementing CDC’s STEADI Falls Prevention Algorithm in Primary Care. The Gerontologist, 57(4), 787–796.
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAYS, INSTRUCTION-COMPLIANT PAPER – DNP 810 Course Papers
DNP 810 Full Course Discussions GCU
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 1 DQ 1
Choose a news story, within last two years, about genetic or genomic technology. What is the issue presented? From the perspective of an RN or APRN, what are the ethical, cultural, religious, legal, fiscal, and societal implications of the issue? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 1 DQ 2
Identify a specific disease encountered in your clinical practice or personal life. Can your patient’s understanding of DNA/RNA replication, transcription, and translation affect the management of the disease? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 2 DQ 1
Identify a complex inheritance health issue you encountered in your clinical practice or personal life. How would you approach working with a patient of a complex inheritance health issue? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 2 DQ 2
Refer to the complex inheritance health issue identified in DQ 1. Given available genetic tests, which would you use to screen and diagnose this issue? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information in practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 3 DQ 1
A multi-generational family health history can facilitate your management of a patient’s disease. What model would you use to create a multi-generational family health history for a patient? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 3 DQ 2
Why is it important to have a comprehensive health and physical assessment that includes information on environment and genomic influences? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information in practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 4 DQ 1
In the past decade there have been many advances in genetics and genomics and their application to health screening, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. What recent advancement do you believe is the most significant for your clinical practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 4 DQ 2
Genetic/genomic factors are known to contribute to variability of pharmacologic responses in some patients. How does the variability of responses result in tailoring pharmacologic agents to the care of these patients? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 5 DQ 1
Health issues in a clinical setting can be influenced by nutrition. Identify a health issue that has been positively influenced by nutrition in your clinic. How does nutrition improve health? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information in practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 5 DQ 2
Choose one disorder of malnutrition that is found in your clinical setting or community. What are the genetic and environmental influences on this disorder, including prevalence rates, testing, treatment, and prognosis? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information into practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 6 DQ 1
What is the impact of the aging population on both increased health care expenditures and wasted resources? Do genetics play a role? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information in practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 6 DQ 2
Identify a method that uses evidence-based data to support new or innovative ways to care for the aging population. What are the anticipated outcomes of employing this method and methods like it? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information in practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 7 DQ 1
What is the impact of chronic disease on both increased health care expenditures and wasted resources? Do genetics play a role? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information in practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 7 DQ 2
Identify a method that uses evidence-based data to support new or innovative ways to care for patients with chronic disease. What are the anticipated outcomes of employing this method and methods like it? How can the doctoral-prepared nurse apply this information in practice? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 8 DQ 1
Choose a news story, within last two years, about genetic or genomic technology. What is the issue presented? From the perspective of an RN or APRN, what are the ethical, cultural, religious, legal, fiscal, and societal implications of the issue? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAYS, INSTRUCTION-COMPLIANT PAPER – DNP 810 Course Papers
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 8 DQ 2
There are several issues that undermine client rights to make genetic and genomic-related decisions and act. Identify two issues you have seen undermine these rights in your clinical setting. What are potential solutions for each? What is your role as the patient advocate with each issue? Explain. Support your rationale with a minimum of two scholarly sources.
DNP 810 Course Papers Assignments GCU
DNP 810 Topic 1 Individual Success Plan (ISP): Part 1
The Individual Success Plan (ISP) assignment in this course requires your collaboration with the course faculty early on to establish a plan for successful completion of mutually identified and agreed upon specific deliverables for your programmatic requirements. Programmatic requirements are: (1) completion of required practice immersion hours, (2) completion of work associated with program competencies, (3) work associated toward completion of your Direct Practice Improvement Project.
DNP 810 Course Papers General Requirements:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment as it pertains to deliverables due in this course:
- Locate and download the Individual Success Plan (ISP) document in the DNP Program Documents folder in the DNP Program Materials section of the DC Network.
- Review the DNP Program Milestones document in the DC Network and identify which milestones apply to this course. Note: Not all courses have milestones.
- Determine what practice experiences you plan to seek to address each competency. Include how many hours you plan to set aside to meet your goals. Learners will apply concepts from each of their core courses to reflect upon, critically examine, and improve current practice, and are required to integrate scholarly readings to develop case reports that demonstrate increasingly complex and proficient practice.
- Use the ISP to develop a personal plan for completing your practice hours and how competencies will be met. Show all the major milestones and deliverables.
Within the ISP, ensure you identify specific deliverables which can include the following: Individualized DNP practice immersion contracts; comprehensive clinical log of hours applied to doctoral level learning outcomes; learner evaluations; mentor evaluations; current and updated CV; scholarly activities; GCU DNP competency self-assessment; reflective journal; course goals and plan for how competencies and practice immersion hours will be met; faculty and mentor approvals of course goals and documented practice immersion hours; and DPI project milestones.
DNP 810 Course Papers Directions:
- Identify the specific deliverables you will complete throughout this course from those defined above or others negotiated with your faculty. You must turn in a new ISP in each course.
- Identify the remaining deliverables you will complete in the upcoming courses.
- List the challenges you expect to encounter as you continue the practice hour and competency requirements throughout this course? How might you overcome these challenges?
- You can renegotiate these deliverables with your faculty throughout this course and update your ISP accordingly.
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- You not are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite.
Complete the Contact Information table at the beginning of the ISP document and type in your signature and the date on which you completed the table.
Read the information in the ISP document including the following:
- Learner Expectations
- Derivation of the ISP
- Instructions for completing the ISP
Follow the instructions and complete the ISP.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 1 Family History
Taking a family history is an important step in determining current and future health needs and education. There are many tools available to complete a comprehensive health history. The Surgeon General’s Family Health History tool is part of the larger Family Health History Initiative that encourages people to talk about and write down health issues that seem to run in the family, bringing a larger focus on this important issue. This assignment allows the learner to use the tool and become familiar with this initiative.
General Guidelines:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
- You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Refer to the LopesWrite Technical Support articles for assistance.
Directions:
Use the “My Family Health Portrait” to document your own family history.
Designate a proband for the pedigree with a disease or condition of interest.
Write a summary (750-1,000 words) of your findings. Include the following information:
- Discuss of the heredity patterns discovered.
- Evaluate the risk of transmission to other/new family members.
- Propose the feasibility of using this tool in your own practice.
It may be possible to earn portfolio practice immersion hours for this assignment. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
Practice Hours Completion Statement DNP-810
I, (INSERT NAME), verify that I have completed (NUMBER OF) clock hours in association with the goals and objectives for this assignment. I also have tracked said practice immersion hours in the Typhon Student Tracking System for verification purposes and will be sure all approvals are in place from my faculty and practice mentor.
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 2 Case Study: Part 1
You will be creating a case study in stages over four course topics. Use an example from your own personal practice, experience, or own personal/family; however, simulated cases are not acceptable for practice hours and therefore not acceptable for this assignment. Examples might include a patient with Duchesne’s muscular dystrophy. Huntington’s disease, Down’s syndrome, sickle cell anemia, BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutations, or other genetic disorder that you and/or the organization in which you practice may specialize in treating.
General Requirements:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
- You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Refer to the LopesWrite Technical Support articles for assistance.
Directions:
For this assignment (Part 1 of the “Case Study”), write a paper (1,000-1,250 words) incorporating genetics information learned from assigned readings in Topics 1 and 2. Include the following:
- Description of the disease, its prevalence, and its incidence.
- Discussion of laboratory testing that is possible.
- Guidelines and reasons behind the FDA regulations for introducing new pharmaceutical agents (policy).
- The role that money and grants play in scientific advances; the economics of health care (capitalism).
- The role and involvement family plays into the health care decision.
It may be possible to earn portfolio practice immersion hours for this assignment. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
Practice Hours Completion Statement DNP-810
I, (INSERT NAME), verify that I have completed (NUMBER OF) clock hours in association with the goals and objectives for this assignment. I also have tracked said practice immersion hours in the Typhon Student Tracking System for verification purposes and will be sure all approvals are in place from my faculty and practice mentor.
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAYS, INSTRUCTION-COMPLIANT PAPER – DNP 810 Course Papers
DNP 810 Course Papers Topic 3 Case Study: Part 2
You will be creating a case study in stages over four course topics. This assignment will add to your previous work in Topic 2. Use an example from your own personal practice, experience, or your own personal/family; however, simulated cases are not acceptable for practice hours and therefore not acceptable for this assignment. Examples might include a patient with Duchesne’s muscular dystrophy. Huntington’s disease, Down’s syndrome, sickle cell anemia, BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutations, or other genetic disorder that you and/or the organization you practice in may specialize in treating.
General Requirements:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA st
READ MORE >>
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCUDNP 815 Course Discussions & ...
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU
DNP 815 Course Discussions & Assignments from GCU Week 1 Discussions
DQ 1
Identify a historical change or event that had significant impact on the development of nursing theory. Discuss the effect of the change/event on nursing from that point forward, the contribution(s) to nursing that resulted, and how it relates now to successfully preparing the DNP for practice.

DQ 2
Provide one definition and an outline of the structure of theory. Debate the purpose of theory and your perspective on the role theory or the lack of theory in today’s nursing practice environment. What purpose (if any) does theory contribute.
DNP 815 Week 2 Discussions
DQ 1
Define the process of theory building. Discuss the differences in approach based on inductive versus deductive reasoning. Describe how you would build and test theory in your practice area.
DQ 2
Select a nursing model or theory described in your textbook. What are the key concepts and components of the example you selected, and how are they defined? Create an example describing the application to an area of nursing practice.
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU DNP 815 Week 3 Discussions
DQ 1
Compare and contrast a minimum of two middle range theories and discuss potential applications in your specific area of nursing practice.
DQ 2
Conduct a literature search in the Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) using the terms middle range theory, mid-range theory, and nursing. Select one of the articles where the development of the middle range theory is the major focus of the paper. Share the article citation and describe how the theory was developed.
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU DNP 815 Week 4 Discussions
DQ 1
Describe a recent or current ethical issue you have faced in nursing practice or which has attained national attention. Discuss the application of ethical theories or principles to the issue. Support the application with sound reasoning.
DQ 2
Consider yourself in a role in which you are accountable for allocation of scarce health care resources for a given situation. Discuss how ethical principles, virtues, and values affect your decision making. Describe your process for ethical decision making. How might a resolution cause conflicts between personal values and beliefs and the perspective of the community or organization?
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU DNP 815 Week 5 Discussions
DQ 1
Learning theories have implications for advanced practice nurses outside the classroom. Share an example describing the application of learning theory or theories to develop a program targeting change to a specific organizational issue, patient lifestyle, or specific unhealthy behaviors.
DQ 2
Health behavior change theories suggest behavior change as a “process,” not an “event.” How can you put this into action for developing an intervention for practice or research? Discuss how you would apply this in planning your DNP project.
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU DNP 815 Week 6 Discussions
DQ 1
Discuss “Envisioning Recovery” as an overarching framework for practice development and focus for all health care treatment.
DQ 2
How can the knowledge of economic theory be utilized by advanced practice nurses? How can economic theory be applied in analysis of interventions?
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU DNP 815 Week 7 Discussions
DQ 1
How can the DNP-prepared nurse apply the concepts of a complex adaptive system to individual patient care? Provide examples.
DQ 2
Research change theories in scholarly literature and on the Internet. Develop a scenario and describe application of a change theory from the perspective of an advanced practice nurse leader.
DNP 815 Course Discussions & Assignments from GCU Week 8 Discussions
DQ 1
Which science-based theories do you think are the most useful to advanced practice nurses, and why?
DQ 2
Explore various science-based theories. Select two theories to describe to your peers. How is each of these theories relevant to application for a DNP-prepared nurse.
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU
DNP 815 Course Discussions & Assignments from GCU Week 1 Individual Success Plan (ISP)
Details:The Individual Success Plan (ISP) assignment requires your collaboration with the course faculty early on to establish a plan for successful completion of mutually identified and agreed upon specific deliverables for your programmatic requirements. Programmatic requirements are: (1) completion of required practice immersion hours, (2) completion of work associated with program competencies, (3) work associated toward completion of your Direct Practice Improvement Project.
General Requirements:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment as it pertains to deliverables due in this course:
- Locate and download the Individual Success Plan (ISP) document in the DNP Program Documents folder in the DNP Program Materials section of the DC Network.
- Review the DNP Program Milestones document in the DC Network and identify which milestones apply to this course. Note: Not all courses have milestones.
- Determine what practice experiences you plan to seek in order to address each competency. Include how many hours you plan to set aside to meet your goals. Learners will apply concepts from each of their core courses to reflect upon, critically examine, and improve current practice. Learners are required to integrate scholarly readings to develop case reports that demonstrate increasingly complex and proficient practice.
- Use the ISP to develop a personal plan for completing your practice hours and for how competencies will be met. Show all of the major milestones and deliverables.
Within the ISP, ensure you identify specific deliverables which can include the following: Individualized DNP practice immersion contracts; comprehensive clinical log of hours applied to doctoral level learning outcomes; learner evaluations; mentor evaluations; current and updated CV; scholarly activities; GCU DNP competency self-assessment; reflective journal; course goals and plan for how competencies and practice immersion hours will be met; faculty and mentor approvals of course goals and documented practice immersion hours; and DPI project milestones.
- Identify the specific deliverables you will complete throughout this course from those defined above or others negotiated with your faculty. You must turn in a new ISP in each course.
- Identify the remaining deliverables you will complete in the upcoming courses.
- List the challenges you expect to encounter as you continue the practice hour and competency requirements throughout this course? How might you overcome these challenges?
- You can renegotiate these deliverables with your faculty throughout this course and update your ISP accordingly.
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
Directions: DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU
Complete the Contact Information table at the beginning of the ISP document and type in your signature and the date on which you completed the table.
Read the information in the ISP document including the following:
- Learner Expectations
- Derivation of the ISP
- Instructions for Completing the ISP
Follow the instructions and complete the ISP.
DNP 815 Course Discussions & Assignments from GCU Week 1 Reflective Analysis Case Report Component Paper
Details:
In this assignment, learners are required to construct a reflective analysis incorporating a personal nursing philosophy which will directly relate to the case report assignment due in Topic 7. As such, learners are encouraged to review the case report assignment requirements in Topic 7 to ensure that the Reflective Analysis Case Report Component Paper will provide the foundational support necessary to complete the Topic 7 assignment successfully. The Reflective Analysis Case Report Component Paper may be written in first-person language as appropriate to express personal perspectives, but must otherwise adhere to the guidelines below.
General Guidelines:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
- You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU Directions:
Compose a 1,000-1,250 word reflective analysis incorporating your personal philosophy of nursing including the following core elements:
- What is your central belief about the individual person?
- How does your personal worldview influence your approach to patients?
- What constitutes the environment?
- How do the individual and the environment interact?
- What is your view of health?
- How does illness relate to health?
- What is the central reason for the existence of nursing?
Portfolio Practice Hours:
It may be possible to earn Portfolio Practice hours for this assignment. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
Practice Hours Completion Statement DNP-815
I, (INSERT NAME), verify that I have completed (NUMBER OF) clock hours in association with the goals and objectives for this assignment. I have also tracked said practice hours in the Typhon Student Tracking System for verification purposes and will be sure that all approvals are in place from my faculty and practice mentor.
DNP 815 Course Discussions & Assignments from GCU Week 2 Topic Selection
DPI Project Milestone: Outline of 10 Strategic PointsDetails: The Direct Practice Improvement (DPI) Project incorporates 10 key or strategic points that need to be clear, simple, correct, and aligned to ensure the project is doable, valuable, and credible. These points, which provide a guide or vision for the project, are present in almost any research.
These 10 points are defined and instructions for completion of the DPI Project Milestone: Outline of 10 Strategic Points assignment are provided in “The 10 Strategic Points for the Prospectus, Proposal, and Direct Practice Improvement Project” resource.Using the table located within the Ten Strategic Points Instructions and Template document, complete the table.
DNP-815-RS-10StrategicPointsfortheProspectusProposalandDPI.docx
Week 3 Conceptual-Theoretical-Empirical Structure (CTE) Evaluation
Details:Conceptual models, theories, and empirical indicators are linked and provide a nursing knowledge system to apply the model or theory to nursing practice, research, and education. Advanced-practice nurses are required to understand the linkages as applied to nursing and translate the components into practice. To continue development of nursing knowledge, advanced practice nurses can create structure to test theory.
General Guidelines:
Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:
- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
- You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
Directions: DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU
Write a 1,000-1,250 word paper examining how the Conceptual – Theoretical – Empirical (CTE) structure translates into nursing practice based on one of the middle range theories that has been formulated or derived from your preferred conceptual model of nursing. Translate and apply the selected theory to nursing practice using actual examples. Evaluate the theory using the CTE steps below:
- Evaluation of the conceptual-theoretical-empirical linkages.
- Evaluation of the selected theory.
- Evaluation of the empirical indicators.
- Evaluation of research findings.
- Evaluation of the utility and soundness of the practice theory.
Portfolio Practice Hours:
It may be possible to earn Portfolio Practice hours for this assignment. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
Practice Hours Completion Statement DNP-815
I, (INSERT NAME), verify that I have completed (NUMBER OF) clock hours in association with the goals and objectives for this assignment. I have also tracked said practice hours in the Typhon Student Tracking System for verification purposes and will be sure that all approvals are in place from my faculty and practice mentor.
DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from Week 7 Case Report: Application of Theory
Details:
In this assignment, learners are required to write a case report addressing the personal knowledge and skills gained in this course and potentially solving an identified practice problem.General Guidelines: Use the following information to ensure successful completion of the assignment:- This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- Doctoral learners are required to use APA style for their writing assignments. The APA Style Guide is located in the Student Success Center.
- This assignment requires that at least two additional scholarly research sources related to this topic, and at least one in-text citation from each source be included.
- You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
Directions: DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU
Construct a 2,500-3,000 word (approximately 10-12 pages) case report that includes a problem or situation consistent with a DNP area of practice.
Requirements:
- Use a minimum of any two theories discussed in the course to develop the case report.
- Apply one or more theories to describe understanding of the problem or situation of focus.
- Apply one or more theories to the recommended intervention or solution being proposed.
- Develop the case report across the entire scenario from the identified clinical or health care problem through proposing an intervention, implementation, and evaluation using an appropriate research instrument.
- Describe the evaluation of the selected research instrument in the case report.
- Lastly, explain in full the tenets, rationale for selection (empirical evidence), and clear application using the language of the theory within the case report.
In addition, your case report must include the following:
- Introduction with a problem statement.
- Brief literature review.
- Description of the case/situation/conditions explained from a theoretical perspective.
- Discussion that includes a detailed explanation of the synthesized literature findings.
- Summary of the case.
- Proposed solutions to remedy gaps, inefficiencies, or other issues from a theoretical approach.
- Identification of a research instrument to evaluate the proposed solution along with a description of how the instrument could be evaluated.
- Conclusion.
Portfolio Practice Hours on DNP 815 Course Discussions Assignments from GCU
It may be possible to earn Portfolio Practice hours for this assignment. Enter the following after the references section of your paper:
Practice Hours Completion Statement DNP-815
I, (INSERT NAME), verify that I have completed (NUMBER OF) clock hours in association with the goals and objectives for this assignment. I have also tracked said practice hours in the Typhon Student Tracking System for verification purposes and will be sure that all approvals are in place from my faculty and practice mentor.
READ MORE >>
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full CourseDNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy ...
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course Module 1 Discussion
DQ1 What is the difference between advocating for health policy directly effecting patients and the community versus advocating for the profession of nursing? Should the nurse health policy advocate only one or the other? How do you imagine the public or legislators would view each set of issues? DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
DQ2 The text discusses little “p†and big “P†policy. Explain the difference between the two.
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 2 Discussion
DQ1 Describe the history of the nursing profession as advocates for health policy and the community; compare with one present day nursing leader in you are acquainted with that demonstrates these same attributes. DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
DQ2 Based on what you have read and your experience is there only one way to advocate based on pre-determined steps in the advocacy process or are there multiple paths to advocacy that depend on the issue and the political environment? DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
ORDER COMPREHENSIVE DNP 820 SOLUTIONS NOW
Module 3 Discussion (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
DQ1 Pick any news article that on the surface is unrelated to health care and make a connection to health based on social or economic issues that if changed could influence health outcomes.
DQ2 Examine a health inequity in your community, state, or nationally and investigate if any changes in health policy has been proposed to address it DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course.
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 4 Discussion (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
DQ1 Choose four nursing organizations. Compare and contrast their legislative agendas. Synthesize the connections between organizational missions and legislative agendas.
DQ2 Evaluate the legislative priorities of four nursing groups. How many focus on the profession of nursing? How many focus on the health of the community? Support your discussion with two peer reviewed articles that evaluate advocacy of the nursing profession versus health patient/community. How does advocating for the nursing profession support healthy outcomes?
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 5 Discussion (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
DQ1 Examine the importance of relationships to move policy forward. Research two articles surrounding this issue and summarize.
DQ2 Give four examples of barriers nurse health policy advocates may face when trying to move health policy forward. Provide examples.
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 6 Discussion (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
DQ1 Evaluate the online resources on page 203 of your text. Which sites are the easiest to navigate? From which sites did you gain the most knowledge on health policy issues in your state and at the federal level?
DQ2 Synthesize the top five issues being debated in health care currently. Apply that knowledge to patient care in your health care organization and/or the community. Will it change care delivery? How?
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy
Module 7 Discussion (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
DQ1 Pick five advocacy actions from the text. Apply them to a health policy issue by briefly describing how you would use these advocacy actions to shape your chosen issue.
DQ2 Reflect on whether health policy is something that happens to you or something you can shape. If it is something that happens to you how could you reconceptulize your role into a health policy shaper?
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy
Module 8 Discussion (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
DQ1 Describe your real-world advocacy strategy to you classmates. Comment and give suggestions.
DQ2 Evaluate the importance of mentors in carrying out your strategy. Do you have one?
Module 1 Assignment
Write a 1500 word APA essay reflecting on:
1. The current nursing culture and whether the bar for nursing leadership is set at the individual patient-nurse relationship or the community-nurse relationship. Give examples of each. Use at least three references to support your findings. DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
2. Review the DNP Essentials and the 2011 Institute of Medicine Future of Nursing Report for statements on nursing leadership in health policy. Identify how these documents define nursing leadership in relation to health policy and the community. Use at least three references to support your findings.
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 2 Assignment
Please submit one APA formatted presentation (PowerPoint®, Prezi®, etc.) of at least 15 slides identifying and describing what health care or professional issue you are passionate about and relay any advocacy actions you took to influence this issue as well as what action you must follow in the future to evaluate if your efforts have had an impact on this issue. The assignment should have a minimum of four scholarly sources, in addition to the textbook.
Complete the Immersion Hours Log, located in the course resource tab, briefly describing your activities consisting of 20 hours for this module and submit with your essay to the dropbox.
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 3 Assignment (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
After researching HP2020, Kaiser Family Foundation, the ANA and your State Board of Nursing:
Please submit one APA formatted presentation (PowerPoint®, Prezi®, etc.) of at least 20 slides identifying and describing how leadership is addressing health disparities. Make certain to include a definition of social justice and evaluate nursing’s role in promotion of social justice. List at least 5-6 references that support your findings. The assignment should have a minimum of four scholarly sources, in addition to the textbook.
Complete the Immersion Hours Log, located in the course resource tab, briefly describing your activities consisting of 20 hours for this module and submit with your essay to the dropbox.
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 4 Assignment
Considering the patient advocacy efforts of the nurse who was unjustly detained for refusing to comply with an unlawful request by law enforcement officers, interview a leader in a health organization eliciting an advocacy story highlighting the power of the nursing voice.
Evaluate the power the nursing organization gives the individual nurse to advocate for health policy. Report on your interview. There is no word count requirement for this assignment, however your response should be fully developed to include context, purpose, core issues, and strategies for a solution.
Based on what you have learned so far this week, create a PowerPoint presentation (minimum 12 slides) with detailed notes for each slide that addresses each of the interview points/questions. Be sure to completely answer all the questions.
Use clear headings that allow your professor to know which bullet you are addressing on the slides in your presentation. Support your content with at least four (4) citations throughout your presentation. Make sure to reference the citations using the APA writing style for the presentation.
Include a slide for your references at the end. Follow best practices for PowerPoint presentations (an example is in the Resources tab) related to text size, color, images, effects, wordiness, and multimedia enhancements DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course.
ORDER COMPREHENSIVE DNP 820 SOLUTIONS NOW
Module 5 Assignment
Research and report on the advocacy process for one health policy issue at your state level. Detail the steps taken to move this issue forward legislatively. Examine the collaboration of interest groups and stakeholders in this process. DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
What were the barriers? Where is this policy issue now? Is it law? Did it fail to pass? Interview nursing leaders/advocates, research articles, and other sources that will bring this process to light. Nursing organizations are valuable resources and have the background stories on these processes, feel free to call and discuss legislative issue with them.
Please submit one APA formatted presentation (PowerPoint®, Prezi®, etc.) of at least 15 slides highlighting your findings. The assignment should have a minimum of four scholarly sources, in addition to the textbook DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course.
Complete the Immersion Hours Log, located in the course resource tab, briefly describing your activities consisting of 20 hours for this module and submit with your essay to the dropbox.
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 6 Assignment (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
Write a 2000 word paper evaluating the PPACA. Detail its timeline from inception to implementation. Analyze the effect the PPACA currently has on access and delivery of healthcare and the anticipated effects it will have on healthcare delivery in the future. What opportunities has the PPACA created for nursing? Describe your state’s position on Medicaid expansion. How has this helped/hurt health care in your state?
Complete the immersion hours form describing your activities consisting of 20 hours this module and submit with your essay to the dropbox. Immersion Hours Log
Module 7 Assignment
This course, you will apply the concepts learned by collaborating with or at least contacting a policy maker about an issue that you think would advance nursing scope, practice or culture or improve patient care and outcomes in a positive way.
Student should research the literature searching for how the nurse can re-conceptualize their role from seeing health policy as “something that happens†to them to “something they can shape†(Institute of Medicine [IOM], 2011, p. S-6).
In Module two, you were asked to describe an issue you hoped to improve and you created a presentation about the plan. This week, you will present on the progress you have made during the past 5 weeks.
This policy change proposal could be with state Board of nursing, local boards, state representatives, or member of Congress/Senate. Based on the issues you selected in Module two, that you are passionate about, researched in depth, and contact with the appropriate policy maker (preferably in person, but at least by email or letter) details of your position and the evidence that supports it, explain your results, determination and outcomes in a 20 slide PowerPoint presentation with audio and speaker notes on all content slides. Make certain to include your sources and a reference slide.
Institute of Medicine. (2011). The future of nursing: Leading change, advancing health.
Complete the immersion hours form describing your activities consisting of 20 hours this module and submit with your presentation to the dropbox. Immersion Hours Log
DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
Module 8 Assignment (DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course)
Presentation:
- The advance practice nurse is preparing to examine the economic, financial, and political factors
- that influence the delivery of healthcare and policy reform. There is a need to develop strategies to influence, implement and evaluate current policy. This presentation will examine a health policy and its influence on a patient population.
- Choose a health policy to evaluate for this presentation and answer the following questions:
- Critically analyze and related issues surrounding the policy from the perspective of consumers, nursing, other health professions, and other stakeholders in policy and public forums.
- What is the role of nursing leadership in the development and implementation of institutional, local, state, federal, and/or international health policy?
- What is the impact of nursing influence on policy makers through their active participation on committees, boards, or task forces at the institutional, local, state, regional, national, and/or international levels to improve health care delivery and outcomes?
- What are some ways that you can do to educate others, including policy makers at all levels, regarding nursing, health policy, and patient care outcomes?
- Analyze the advocacy process for the nursing profession within the policy and healthcare communities that relate to your selected policy.
- Explain nursing responsibility to develop, evaluate, and provide leadership for health care policy that shapes health care financing, regulation, and delivery.
- Identify the connection between health outcomes and advocacy for social justice, equity, and ethical policies within all healthcare arenas for your selected policy.
- This PowerPoint® (Microsoft Office) or Impress® (Open Office) presentation should be a minimum of 20 slides, including a title and reference slide, with detailed speaker notes on content slides and recorded audio. Use at least four scholarly sources and make certain to review the module’s Signature Assignment Rubric before starting your presentation. This presentation is worth 400 points for a quality content and presentation.
- Lastly, complete the immersion hours form describing your activities consisting of 80 immersion hours during this class, obtain your instructor’s signature as verification of completion and submit with your submission to the dropbox. DNP 820 Health Policy and Advocacy Full Course
READ MORE >>
graphs etc to diagram your ideas.My Project is a quality improvement project to ...
My Project is a quality improvement project to increase awareness among primary care providers on Prediabetes screening
**If your project is not a QI project you may use a sample idea such as decreasing transmission of COVID-19 by proper hand washing.
Module 2 Discussion: Clinical Data Analytics
Read the documents related to Clinical Analytics found in this Module. (1. Clinical Analytics Basics.PDF and 2. Healthcare Data Analytics 2018.PDF) Using your project idea or concept
READ MORE >>