Our Previous Samples
Case Study: Contraception OptionsCase Study: Contraception Options Scenario 1Ela ...
Case Study: Contraception Options
Case Study: Contraception Options Scenario 1
Elaine Goodwin is a 38-year-old G5 P5 LC 6?presenting to your clinic today to discuss contraceptive options.??She states that she is not interested in having more children?but her new partner has never fathered a child.?Her medical history is?remarkable for exercise-induced asthma, migraines, and IBS.?Her surgical history?is remarkable only for tonsils as a child. Case Study: Contraception Options
Her social history is negative for?alcohol, tobacco, and recreational drugs.? She has no known drug allergies and takes only vitamin C.?Hospitalizations were only for childbirth.?Family history?reveals that her maternal grandmother is alive with dementia, while her maternal grandfather is alive with COPD. Her paternal grandparents are both deceased?due to an automobile accident.
Her mother is alive with osteopenia and fibromyalgia, and her dad is alive with a history of skin cancer (basal cell).?Elaine has one older sister with no medical problems and one younger brother with no reported medical problems Case Study: Contraception Options.
ORDER COMPREHENSIVE SOLUTION PAPERS ON Case Study: Contraception Options
- Height 5’ 7”?Weight?148?(BMI 23.1),?BP 118/72 P?68
- HEENT:? wnl
- Neck: supple without adenopathy
- Lungs/CV: wnl
- Breast: soft, fibrocystic changes bilaterally,?without masses, dimpling or discharge
- Abd: soft, +BS, no tenderness
- VVBSU: wnl, except?1st?degree cystocele
- Cervix: firm, smooth, parous, without CMT
- Uterus: RV, mobile,?non-tender,?approximately 10 cm,
- Adnexa: without masses or tenderness
QUESTION:
What other information do you need?
MORE QUESTIONS:
- What has she used in the?past?? Why did she stop a?method?? How many partners in past 12?months?
- What are her current cycles like?
- When was her last gyn exam?and what were the results of?the?tests?
- Are her migraines with or without auras?
- What method has she considered.
QUESTIONS:
•What are your next steps/considerations?
•;What teaching should you do?
•What methods are appropriate for Elaine?
NRNP 6552: Advanced Nurse Practice in Reproductive Health Care
Episodic/Focused SOAP Note Template
Patient Information:
Initials, Age, Sex, Race
S.
CC (chief complaint): This is a brief statement identifying why the patient is here in the patient’s own words, for instance, “headache,” not “bad headache for 3 days.” Case Study: Contraception Options
HPI: This is the symptom analysis section of your note. Thorough documentation in this section is essential for patient care, coding, and billing analysis. Paint a picture of what is wrong with the patient. Use LOCATES Mnemonic to complete your HPI. You need to start every HPI with age, race, and gender (e.g., 34-year-old African American male). You must include the seven attributes of each principal symptom in paragraph form, not a list. If the CC was “headache,” the LOCATES for the HPI might look like the following example:
Location: head
Onset: 3 days ago
Character: pounding, pressure around the eyes and temples
Associated signs and symptoms: nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia
Timing: after being on the computer all day at work
Exacerbating/relieving factors: light bothers eyes, Naproxen makes it tolerable but not completely better
Severity: 7/10 pain scale
Current Medications: Include dosage, frequency, length of time used, and reason for use. Also include over-the-counter (OTC) or homeopathic products.
Allergies: Include medication, food, and environmental allergies separately. Provide a description of what the allergy is (e.g., angioedema, anaphylaxis). This will help determine a true reaction versus intolerance.
PMHx: Include immunization status (note date of last tetanus for all adults), past major illnesses, and surgeries. Depending on the CC, more info is sometimes needed. Soc & Substance Hx: Include occupation and major hobbies, family status, tobacco and alcohol use (previous and current use), and any other pertinent data. Case Study: Contraception Options
Always add some health promotion questions here, such as whether they use seat belts all the time or whether they have working smoke detectors in the house, the condition of the living environment, text/cell phone use while driving, and support systems available.
Fam Hx: Illnesses with possible genetic predisposition, contagious illnesses, or chronic illnesses. The reason for death of any deceased first-degree relatives should be included. Include parents, grandparents, siblings, and children. Include grandchildren if pertinent. Case Study: Contraception Options
Surgical Hx: Prior surgical procedures.
Mental Hx: Diagnosis and treatment. Current concerns: (Anxiety and/or depression). History of self-harm practices and/or suicidal or homicidal ideation.
Violence Hx: Concern or issues about safety (personal, home, community, sexual—current and historical).
Reproductive Hx: Menstrual history (date of last menstrual period [LMP]), pregnant (yes or no), nursing/lactating (yes or no), contraceptive use (method used), types of intercourse (oral, anal, vaginal, other), and any sexual concerns. Case Study: Contraception Options
ROS: This covers all body systems that may help you include or rule out a differential diagnosis. You should list each system as follows: General: Head: EENT: and so forth. You should list these in bullet format and document the systems in order from head to toe.
Example of Complete ROS:
GENERAL: No weight loss, fever, chills, weakness, or fatigue.
HEENT: Eyes: No visual loss, blurred vision, double vision, or yellow sclerae. Ears, Nose, Throat: No hearing loss, sneezing, congestion, runny nose, or sore throat.
SKIN: No rash or itching.
CARDIOVASCULAR: No chest pain, chest pressure, or chest discomfort. No palpitations or edema.
RESPIRATORY: No shortness of breath, cough, or sputum.
GASTROINTESTINAL: No anorexia, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. No abdominal pain or blood.
GENITOURINARY: Burning on urination. Pregnancy. LMP: MM/DD/YYYY.
NEUROLOGICAL: No headache, dizziness, syncope, paralysis, ataxia, numbness, or tingling in the extremities. No change in bowel or bladder control.
MUSCULOSKELETAL: No muscle pain, back pain, joint pain, or stiffness.
HEMATOLOGIC: No anemia, bleeding, or bruising.
LYMPHATICS: No enlarged nodes. No history of splenectomy.
PSYCHIATRIC: No history of depression or anxiety.
ENDOCRINOLOGIC: No reports of sweating or cold or heat intolerance. No polyuria or polydipsia.
REPRODUCTIVE: Not pregnant and no recent pregnancy. No reports of vaginal or penile discharge. Not sexually active.
ALLERGIES: No history of asthma, hives, eczema, or rhinitis.
O.
Physical exam: From head to toe, include what you see, hear, and feel when conducting your physical exam. You only need to examine the systems that are pertinent to the CC, HPI, and history. Do not use “WNL” or “normal.” You must describe what you see. Always document in head-to-toe format (i.e., General: Head: EENT:) Case Study: Contraception Options
Diagnostic results: Include any labs, x-rays, or other diagnostics that are needed to develop the differential diagnoses (support with evidenced and guidelines).
A.
Differential Diagnoses (list a minimum of 3 differential diagnoses). Your primary or presumptive diagnosis should be at the top of the list. For each diagnosis, provide supportive documentation with evidence-based guidelines. Case Study: Contraception Options
P.
Includes documentation of diagnostic studies that will be obtained, referrals to other health care providers, therapeutic interventions, education, disposition of the patient, and any planned follow-up visits. Each diagnosis or condition documented in the assessment should be addressed in the plan. The details of the plan should follow an orderly manner. Also included in this section is the reflection. The student should reflect on this case and discuss whether or not they agree with their preceptor’s treatment of the patient and why or why not. What did they learn from this case? What would they do differently?
Also include in your reflection a discussion related to health promotion and disease prevention, taking into consideration patient factors (e.g., age, ethnic group), PMH, and other risk factors (e.g., socioeconomic, cultural background). Case Study: Contraception Options
Case Study: Contraception Options References
You are required to include at least three evidence-based, peer-reviewed journal articles or evidenced-based guidelines that relate to this case to support your diagnostics and differentials diagnoses. Be sure to use correct APA 7th edition formatting. Case Study: Contraception Options
READ MORE >>
Case study Diabetes Sample PaperIntroductionDiabetes is a chronic condition char ...
Case study Diabetes Sample Paper
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated glucose levels resulting from failure of production of the hormone insulin from the pancreas or failure to effectively utilise the insulin produced (Rafacho et al., 2017). Due to adoption of a sedentary lifestyle by majority of the people globally, there has been an increase in the number of diabetes cases reported. Elevated blood glucose that is not controlled causes marked damage to majority of the body’s organ systems.
Primary diagnosis.
The primary diagnosis is diabetes. Elevated glucose levels circulating in blood normally presents with increased thirst and urgency of urination, fatigue and blurred vision. The patient is markedly obese weighing 185 pounds and has a history of alcohol consumption taking 1-2 glasses on weekends. There is a small amount of protein in the patient’s urine. The pertinent negative findings include normal pulse rate and blood pressure (Whelton, et al., 2018). Absence of ketones is another negative finding. There is also no history of diabetes in the patient’s family. The patient presented with fatigue, increased thirst, nocturia and weight gain. Glucosuria and proteinuria confirm the diagnosis of diabetes.
Secondary findings.
Anaemia can be one of the secondary findings. This results from an imbalance in red blood cells destruction in comparison to their production. Positive pertinent findings include fatigue. Negative pertinent findings include the absence of headaches and no shortness of breath (Hakim et al., 2017). The presence of fatigue and slightly reduced haemoglobin levels below the normal range are indicative of anaemia.
Diagnostics.
Random Plasma Glucose Test is one of the first laboratory tests to order. This test is used to diagnose diabetes when the symptoms are present (Punthakee et al.,2018). The patient does not need to have fasted for this test to be conducted. This blood test can be done at any time. Glucose levels above 200 mg/dl when a RBS test is done is indicative of diabetes mellitus. Fasting Plasma Glucose Test is another confirmatory test for diabetes. This test measures blood glucose levels at a particular time and is most suited to be conducted in the morning (American Diabetes Association, 2017). This is after a fast of about eight hours without intake of any food or drinks. Blood glucose levels of more than 126mg/dl on two separate tests is indicative of diabetes.
The haemoglobin A1C test is another test used in the diagnosis of diabetes. This test provides the average blood sugar levels over a period of around three months (American Diabetes Association, 2017). The test, also referred to as glycosylated haemoglobin test, is conducted after a period of fasting where the patient is advised not to eat or drink before the test. The doctor takes into consideration several factors such as the patient’s age or whether the patient has anaemia. This is because the test is likely to give inaccurate results in anaemia patients. A 6.5% result and above is indicative of diabetes.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) is also used in the diagnosis of diabetes. A health care professional is first tasked with the duty of drawing blood. After this, the patient drinks a liquid containing glucose and the health care worker draws blood after one hour and again after two hours. This test is however more expensive when compared to the other tests. Glucose levels above 200mg/dl indicate diabetes. Complete blood count should also be conducted. The patient’s haemoglobin level is 12.5 g/dl. This is below the normal range in males. Subsequent tests should be done to monitor and to ensure that the levels do not drop further as this can lead to severe anemia (Mazer et al., 2017). Anaemia gradually develops in people with diabetes due to kidney damage which consequently interferes with erythropoietin production that is essential in red blood cell formation.
Medications.
One of the drugs to be used is acarbose. 25 g of Precose taken PO 3 times a day (q8hr) at meals is recommended. The dose can gradually be raised to 50 or 100 g taken PO 3 times a day. This drug lowers the rate of food breakdown to glucose ensuring that there is no sudden rise in blood glucose levels after a meal. Metformin is another drug used in the treatment of diabetes. It is the recommended drug for type 2 diabetes (Sanchez-Rangel et al, 2017). The initial dosage of the drug is 500 mg orally every 12 hours or 800 mg orally taken once a day with meals. This is gradually increased every two weeks with a maintenance dosage of 1500 to 2550mg orally taken once every 8-12 hours with meals. Caution is taken not to administer more than 2550 mg every day.
For the management of anaemia, iron supplements are indicated to counter iron deficiency. Ferrous sulphate is the main supplement used to counter anaemia. 65 g of iron sulphate taken 3 times a day are recommended though 15-20 g have proven to be as effective with fewer side effects (Pereira et al., 2018). 500 units of Vitamin C taken once daily have shown to increase absorption of iron sulphate.
Education.
i)Diagnosis.
Inform the patient that his symptoms are indicative of diabetes. The increased passing of urine is because of increased urine production, which reflects the body’s attempt to excrete the extra glucose. This increased loss of fluids leads to an increased urge to replace the lost fluid resulting in the increased thirst. The elevated blood glucose levels are also responsible for the fatigue being experienced. The excess weight gain is because of increased food uptake resulting in elevated glucose levels that are deposited in tissues as fat causing the weight gain.
ii)Medication.
Metformin used acts as a metabolic inhibitor and causes a change in energy breakdown to glucose, thus lowering the blood glucose levels. The drug is the mainstay treatment of type 2 diabetes. The drug however has several side effects that include the risk of hypoglycaemia, abdominal discomfort, upper respiratory tract infections, physical weakness, diarrhoea, reduced levels of Vitamin B-12 and lactic acidosis (Sanchez-Rangel et al., 2017). Acarbose is another drug used for type two diabetes. It works by slowing down the action of chemicals responsible for the breakdown of food to produce glucose and consequently stops a sudden spike in blood glucose after a meal. The drug, however, has several side effects that include abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, bloating. Other side effects which are rare include rectal bleeding, unusual fatigue, yellowing of the eyes and darkly colored urine.
Ferrous sulphate is used to counter iron deficiency anemia. These medications work by replacing body iron. Iron is essential for the production of red blood cells. Some of the side effects associated with ferrous sulphate include constipation, diarrhea, dark stools, gastrointestinal irritation and obstruction (Pereira et al., 2018). Gastrointestinal hemorrhage and perforation may occur in some rare instances. It is therefore vital to monitor for the emergence of these side effects and inform the healthcare professional.
iii)Diet.
The patient should consume a diet comprising of non-starchy vegetables such as broccoli, carrots, peppers, tomatoes and other green leafy vegetables. Starchy vegetables such as potatoes and corn are also highly recommended. Patient should also be advised to take fruits such as oranges, lemons, apples and berries. Grains including wheat and rice are also highly recommended. Lean meat, eggs, fish and nuts among other rich protein sources are also recommended (Tan, 2019).
Green leafy vegetables, liver and seafoods are recommended to counter the anemia. Patient should also take plenty of water. It is critical for the patient to alter his diet as he is obese. He should take meals at regular intervals and avoid snacking. Losing between ten and fifteen pounds can go a long way in managing the patient’s weight for better outcomes. A good diet plan coupled with regular exercise can go a long way in enabling the patient lose weight.
iv)Exercise.
Diabetes predisposes most patients to cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular exercises also referred to as aerobic exercises are highly recommended in diabetes patients. These exercises include walking, swimming, cycling, jogging and dancing. It is recommended that the patient completes about thirty minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity exercise for at least five days in a week (Liguori, 2020). This helps in lowering the body weight and regulating the blood pressure.
v)Warning Signs of Diagnosis.
If left unchecked, the diabetes may result in cardiovascular disease, damage to the nerves, kidney injury, eye damage which may potentially cause blindness, and damage to the feet causing serious infections in the case of cuts or blisters. Other complications that may emerge include hearing impairment and increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease that may lead to depression. As observed by Clare (2017). anemia left unchecked can cause cardiovascular complications. Prolonged metformin use can lead to lactic acidosis which is a serious condition characterized by lactic acid accumulation in the blood. Prolonged use of ferrous sulphate leads to gastric hemorrhage and perforation which can predispose one to sepsis, malnutrition, adhesions and bowel obstruction, delirium and in the worst-case scenario, multiorgan failure.
Referral.
An endocrinologist is key in helping the patient with his treatment plan. An ophthalmologist may also be needed since individuals suffering from diabetes regularly experience complications with their eyes including cataracts, glaucoma and diabetic neuropathy. A nephrologist is needed as diabetic patients are predisposed to developing kidney complications. A dietician will help with recommending the appropriate diet for the patient.
Follow up.
It is advisable for the patient to visit the healthcare professional after one month. This is to ensure that the patient has been compliant to his medication and has adhered to his diet and exercise plan. Studies such as that of Li et al. (2020) among others have shown that a number of patients are often non-compliant and it is therefore critical to see them regularly in order to educate them about their condition and further assess their compliance.
Assessment of comorbidities.
It is critical to first confirm and classify the diabetes the patient has. Next is to detect any complications and potential comorbid conditions that may arise from the diabetes. As Norhammar et al. (2019) observes, it is important to review the previous treatment and risk factor control in patients with established diabetes. After these steps, one can then begin to engage the patient with the goal of formulating a care management plan to enable provision of continuing care.
Medication Cost.
Topol (2019) estimates that individuals suffering from diabetes incur an average cost of 16732 dollars annually in medical expenditure. This cost is distributed among inpatient hospital care which uses around 30%, and prescription medications which translate to about 30% of the total cost. Further, antidiabetic agents and doctor office visits account for 15% and 13% of the total cost respectively.
Conclusion
Diabetes incidence has gradually increased over the years due to sedentary lifestyles. Diabetes is associated with several complications including cardiovascular injury, kidney damage and damage to the eyes. It is therefore critical to prevent and manage diabetes in order to avoid the complications it is associated with and also to reduce the cost of management which is quite high. Adoption of a good diet plan and regular exercise helps to prevent the development of diabetes and also helps in management of those with diabetes and consequently reduces complications.
References.
- American Diabetes Association. (2017). 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes care, 40(Supplement 1), S11-S24. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc17-S005
- Clare, E. (2017). Brilliant imperfection: Grappling with cure. Duke University Press.
- Hakim, A., De Wandele, I., O’Callaghan, C., Pocinki, A., & Rowe, P. (2017, March). Chronic fatigue in Ehlers–Danlos syndrome—Hypermobile type. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C: Seminars in Medical Genetics, 175(1), 175-180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31542
- Li, J-P. O., Liu, H., Ting, D. S. J., Jeon, S., Chan, R. V. P., Kim, J. E., Sim, D. A., Thomas, P. B. M., Lin, H., Chen, Y., Sakomoto, T., Loewenstein, A., Lam, D. S. C., Pasquale, L. R., Wong, T. Y., Lam, L. A., & Ting, D. S. W., (2020). Digital technology, tele-medicine and artificial intelligence in ophthalmology: A global perspective. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, (), 100900–. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100900
- Liguori, G., (2020). ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Mazer, C. D., Whitlock, R. P., Fergusson, D. A., Hall, J., Belley-Cote, E., Connolly, K., Khanykin, B., Gregory, A. J., de Médicis, É., McGuinness, S., Royse, A., Carrier, F. M., Young, P. J., Villar, J. C., Grocott, H. P., Seeberger, M. D., Fremes, S., Lellouche, F., Syed, S., … Shehata, N. (2017). Restrictive or Liberal Red-Cell Transfusion for Cardiac Surgery. New England Journal of Medicine, (), NEJMoa1711818–. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1711818
- Norhammar, A., Kjellström, B., Habib, N., Gustafsson, A., Klinge, B., Nygren, Å., Näsman, P., Svenungsson, E., & Rydén, L. (2019). Undetected Dysglycemia Is an Important Risk Factor for Two Common Diseases, Myocardial Infarction and Periodontitis: A Report From the PAROKRANK Study. Diabetes Care, 42(8), 1504–1511. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-0018
- Pereira, D. I., Mohammed, N. I., Ofordile, O., Camara, F., Baldeh, B., Mendy, T., Sanyang, C., Jallow, A. T., Hossain, I., Wason, J. & Prentice, A. M. (2018). A novel nano-iron supplement to safely combat iron deficiency and anaemia in young children: The IHAT-GUT double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial protocol. Gates Open Research, 2, 48. https://dx.doi.org/10.12688%2Fgatesopenres.12866.2
- Punthakee, Z., Goldenberg, R., & Katz, P. (2018). Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes, prediabetes and metabolic syndrome. Canadian Journal Of Diabetes, 42, S10-S15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.10.003
- Rafacho, A., Ortsäter, H., Nadal, A., & Quesada, I. (2017). Glucocorticoid treatment and endocrine pancreas function: implications for glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance and diabetes Journal of Endocrinology, 223(3), R49–R62. doi:10.1530/JOE-14-0373
- Sanchez-Rangel, E., & Inzucchi, S. E. (2017). Metformin: clinical use in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia, 60(9), 1586-1593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-017-4336-x
- Tan, G. S. (2019). Nutrition Education Modules for Nurses. Accessed April 2nd 2020 from https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/creativecomponents/259/
- Topol, E. (2019). Deep medicine: how artificial intelligence can make healthcare human again. Hachette UK.
- Whelton, P. K., Carey, R. M., Aronow, W. S., Casey, D. E., Collins, K. J., Dennison H. C., DePalma, S. M., Gidding, S., Jamerson, K. A., Jones, D. W., MacLaughlin, E. J., Muntner, P., Ovbiagele, B., Smith, S. C., Spencer, C. C., Stafford, R. S., Taler, S. J., Thomas, R. J., Williams, K. A., … Wright, J. T. (2018). 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 71(19), e127-e248. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYP.0000000000000065
READ MORE >>
Case Study: Mr JD is a 24-year-old who presents to Urgent Care with a 2-week his ...
Case Study: Mr JD is a 24-year-old who presents to Urgent Care with a 2-week history of cough and congestion
Case Study: Mr JD is a 24-year-old who presents to Urgent Care with a 2-week history of cough and congestion.
For this questions, please read the following case study and then respond to the questions noted below.
Mr. JD is a 24-year-old who presents to Urgent Care with a 2-week history of cough and congestion. He says it started out as a ”normal cold” and it will not go away. He has a productive cough for green mucous and has green nasal discharge. He says he has had a low-grade temperature for the past 2 days. John reports an intermittent frontal headache with this cold. He is otherwise healthy, with no known allergies.
In his assessment it is found that his vital signs are stable, temperature is 99.9 degrees F, tympanic membranes (TMs) are clear bilaterally, pharynx is erythematous with no exudate; there is greenish postnasal drainage; turbinates are swollen and red; frontal sinus tenderness; no cervical adenopathy, and lungs are clear bilaterally.
- Is there any additional subjective or objective information you need for this client? Explain.
Would you treat Mr. JDs cold? Why or why not? - What would you prescribe and for how many days? Include the class of the medication, mechanism of action, route, the half-life; how it is metabolized in and eliminated from the body; and contraindications and black box warnings.
- Would this treatment vary if Mr. JD was a 10 year-old 78 lb child? Include the class of the medication, mechanism of action, dosing, route, the half-life; how it is metabolized in and eliminated from the body; and contraindications and black box warnings
- What health maintenance or preventive education is important for this client based on your choice medication/treatment?
Case Study: Mr JD is a 24-year-old who presents to Urgent Care with a 2-week history of cough and congestion – Instructions
You must proofread your paper. But do not strictly rely on your computer’s spell-checker and grammar-checker; failure to do so indicates a lack of effort on your part and you can expect your grade to suffer accordingly. Papers with numerous misspelled words and grammatical mistakes will be penalized.
Read over your paper – in silence and then aloud – before handing it in and make corrections as necessary. Often it is advantageous to have a friend proofread your paper for obvious errors. Handwritten corrections are preferable to uncorrected mistakes.
Use a standard 10 to 12 point (10 to 12 characters per inch) typeface. Smaller or compressed type and papers with small margins or single-spacing are hard to read. It is better to let your essay run over the recommended number of pages than to try to compress it into fewer pages.
Likewise, large type, large margins, large indentations, triple-spacing, increased leading (space between lines), increased kerning (space between letters), and any other such attempts at “padding” to increase the length of a paper are unacceptable, wasteful of trees, and will not fool your professor.
The paper must be neatly formatted, double-spaced with a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, and sides of each page. When submitting hard copy, be sure to use white paper and print out using dark ink. If it is hard to read your essay, it will also be hard to follow your argument.
ADDITIONAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE CLASS
Discussion Questions (DQ)
- Initial responses to the DQ should address all components of the questions asked, include a minimum of one scholarly source, and be at least 250 words.
- Successful responses are substantive (i.e., add something new to the discussion, engage others in the discussion, well-developed idea) and include at least one scholarly source.
- One or two sentence responses, simple statements of agreement or “good post,” and responses that are off-topic will not count as substantive. Substantive responses should be at least 150 words.
- I encourage you to incorporate the readings from the week (as applicable) into your responses.
Weekly Participation
- Your initial responses to the mandatory DQ do not count toward participation and are graded separately.
- In addition to the DQ responses, you must post at least one reply to peers (or me) on three separate days, for a total of three replies.
- Participation posts do not require a scholarly source/citation (unless you cite someone else’s work).
- Part of your weekly participation includes viewing the weekly announcement and attesting to watching it in the comments. These announcements are made to ensure you understand everything that is due during the week.
APA Format and Writing Quality
- Familiarize yourself with APA format and practice using it correctly. It is used for most writing assignments for your degree. Visit the Writing Center in the Student Success Center, under the Resources tab in LoudCloud for APA paper templates, citation examples, tips, etc. Points will be deducted for poor use of APA format or absence of APA format (if required).
- Cite all sources of information! When in doubt, cite the source. Paraphrasing also requires a citation.
- I highly recommend using the APA Publication Manual, 6th edition.
Use of Direct Quotes
- I discourage overutilization of direct quotes in DQs and assignments at the Masters’ level and deduct points accordingly.
- As Masters’ level students, it is important that you be able to critically analyze and interpret information from journal articles and other resources. Simply restating someone else’s words does not demonstrate an understanding of the content or critical analysis of the content.
- It is best to paraphrase content and cite your source.
LopesWrite Policy
- For assignments that need to be submitted to LopesWrite, please be sure you have received your report and Similarity Index (SI) percentage BEFORE you do a “final submit” to me.
- Once you have received your report, please review it. This report will show you grammatical, punctuation, and spelling errors that can easily be fixed. Take the extra few minutes to review instead of getting counted off for these mistakes.
- Review your similarities. Did you forget to cite something? Did you not paraphrase well enough? Is your paper made up of someone else’s thoughts more than your own?
- Visit the Writing Center in the Student Success Center, under the Resources tab in LoudCloud for tips on improving your paper and SI score.
Late Policy
- The university’s policy on late assignments is 10% penalty PER DAY LATE. This also applies to late DQ replies.
- Please communicate with me if you anticipate having to submit an assignment late. I am happy to be flexible, with advance notice. We may be able to work out an extension based on extenuating circumstances.
- If you do not communicate with me before submitting an assignment late, the GCU late policy will be in effect.
- I do not accept assignments that are two or more weeks late unless we have worked out an extension.
- As per policy, no assignments are accepted after the last day of class. Any assignment submitted after midnight on the last day of class will not be accepted for grading.
Communication
Communication is so very important. There are multiple ways to communicate with me:
- Questions to Instructor Forum: This is a great place to ask course content or assignment questions. If you have a question, there is a good chance one of your peers does as well. This is a public forum for the class.
- Individual Forum: This is a private forum to ask me questions or send me messages. This will be checked at least once every 24 hours.
READ MORE >>
Herzing NU621 Unit 4 Discussion Advanced Pathophysiology: Case Study: Patient wi ...
Herzing NU621 Unit 4 Discussion Advanced Pathophysiology: Case Study: Patient with lower abdominal discomfort nausea
Digestive Function
Read the following case study and answer the posed questions
Case #1: A 64-year-old man presents to the emergency department (Links to an external site.) with abdominal pain and distention, as well as constipation of 8 days’ duration. He denies vomiting, fever, diarrhea, or dysuria. Except for hypertension, he is otherwise healthy with no prior surgeries. Case Study: Patient with lower abdominal discomfort nausea
His vital signs are normal except for a borderline pulse of 99 bpm. His physical examination is unremarkable except for his abdomen, which is large, rotund, and tympanitic. There is diffuse tenderness everywhere in the abdomen Case Study: Patient with lower abdominal discomfort nausea.
What history would you want to obtain?
What differential diagnoses would you consider?
List and describe the specific diagnostic tests you might order to determine cause of his concern?
ORDER COMPREHENSIVE NU621 SOLUTIONS NOW
Case #2:
Kyle is a 58-year-old man who is experiencing lower abdominal discomfort nausea and diarrhea lasting 2 days. He thought he had eaten something that “disturbed his stomach” but since this has lasted so long, he is afraid it’s something serious.
As you obtain a history from this patient what differential diagnoses are you considering. Give rational for your choices.
Discuss the pathophysiologic relationship between nausea and vomiting?
Three days after Kyle’s initial visit his labs confirmed a diagnosis of cirrhosis.
Discuss the pathophysiologic relationship between cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
Cite current research findings, national guidelines, and expert opinions and controversies found in the medical and nursing literature to support your position and suggestions. Case Study: Patient with lower abdominal discomfort nausea
Responses need to address all components of the question, demonstrate critical thinking and analysis, and include peer reviewed journal evidence to support the student’s position.
Please be sure to validate your opinions and ideas with citations and references in APA format.
Please review the rubric to ensure that your response meets the criteria.
Estimated time to complete: 2 hours
Discussion Peer/Participation Prompt [Due Sunday]
Please respond to at least 2 of your peer’s posts. To ensure that your responses are substantive, use at least three of these prompts:
- Do you agree with your peers’ diagnosis?
- Take an alternate view and offer a potential alternate approach.
- Share your thoughts on how you support their opinion and explain why.
- Present new references that support your opinions.
- Responses need to address all components of the question, demonstrate critical thinking and analysis, and include peer reviewed journal evidence to support the student’s position.
- Case Study: Patient with lower abdominal discomfort nausea
Intermittent Abdominal Pain Example
Today, an 18-year-old Caucasian female appears with intermittent stomach pain. She also has a low-grade fever, cramps, and diarrhea. She has also lost her appetite. She acknowledges smoking 1/2 PPD for two years. Denies using illegal drugs or alcohol and reports a Crohn’s disease history.
Differential Diagnosis
The top differentials I would consider include Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and appendicitis. The inflammatory bowel diseases Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) have an immunological basis (Ranasinghe & Hsu, 2022). The trajectory of Crohn’s disease is one of remission and relapse. Typical symptoms of Crohn’s disease flare-ups include stomach discomfort, bloating, diarrhea, fever, weight loss, and anemia. Many of the manifestations can be seen in the patient. Ulcerative colitis is an inflammation of the colon that has no known cause.
Bloody diarrhea, whether it contains mucus or not, is the predominant sign. Depending on how far the illness has spread and how bad it is, one may also have tenesmus, malaise, abdominal pain, weight loss, and fever (Lynch & Hsu, 2023). The condition usually worsens over time, and people with it often go through periods of remission followed by relapses. When the vermiform appendix gets inflamed, this is called appendicitis. According to research, anorexia and periumbilical pain are common symptoms of appendicitis, and they frequently precede right lower quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and other symptoms (Echevarria et al., 2023). Crohn’s disease is, therefore, the presumptive diagnosis.
Focused Physical Examination
It would be useful for the patient with a suspected Crohn’s disease flare-up to have several targeted physical exam results. After visually inspecting the patient’s abdomen, all four quadrants should be auscultated to listen for any altered bowel sounds that might indicate obstruction. After that, the abdomen should be palpated to check for organomegaly, ascites, rebound pain, or distention (Ranasinghe & Hsu, 2022). All patients require a perineum exam. Skin tags, fistulas, scars, ulcers, and abscesses could all be seen during the examination.
Diagnostic testing to confirm the diagnosis
A thorough investigation is required for diagnosis confirmation. Infections can be ruled out by stool tests for culture, ovum and parasites, C. difficile toxins, leukocyte count, and calprotectin, which can identify active Crohn’s disease. It is possible to differentiate between Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis using blood tests such as the CBC, metabolic panel, ANCA, and ASCA. CRP or ESR indicates how severe the inflammation is (Kedia et al., 2019; Ranasinghe & Hsu, 2022). While plain X-rays can reveal intestinal obstruction, imaging techniques like CT scan/MRE of small bowel follow-through and VCE can see the afflicted areas.
Evidence-based treatment Approach
Crohn’s disease should be treated with a multidisciplinary approach based on the patient’s needs. Evidence-based treatment guidelines suggest that people with Crohn’s disease may need to take medicine and change their lifestyle. Anti-inflammatory drugs like aminosalicylates or corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in the bowel (Ranasinghe & Hsu, 2022).
Immune system suppressors like azathioprine or methotrexate stop the immune system from attacking the bowel. Anti-TNF drugs like infliximab, adalimumab, and golimumab block TNF to stop it from causing inflammation (Ranasinghe & Hsu, 2022). Nutritional support, such as a low-residue or elemental diet, is required to give the bowel time to recover. Smoking cessation and stress management are two lifestyle changes that can help to lessen flare-ups.
References
Echevarria†, S., Rauf†, F., Hussain†, N., Zaka, H., Farwa, U. -, Ahsan, N., Broomfield, A., Akbar, A., & Khawaja, U. A. (2023). Typical and atypical presentations of appendicitis and their implications for diagnosis and treatment: A literature review. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.37024
Jones, M. W., Lopez, R. A., & Deppen, J. G. (2022). Appendicitis. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493193/#:~:text=Appendicitis%20is%20the%20inflammation%20of
Kedia, S., Das, P., Madhusudhan, K. S., Dattagupta, S., Sharma, R., Sahni, P., Makharia, G., & Ahuja, V. (2019). Differentiating Crohn’s disease from intestinal tuberculosis. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 25(4), 418–432. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i4.418
Lynch, W. D., & Hsu, R. (2023). Ulcerative colitis. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459282/#:~:text=Introduction-
Ranasinghe, I. R., & Hsu, R. (2022, May 15). Crohn disease. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436021/
Abdominal Assessment Soap Note
The episodic SOAP note is of a 65-year-old African American male with epigastric pain.
Subjective Portion
The objective portion of the episodic SOAP note contained the chief complaint, history of presenting illness, past medical history, medication history, allergies, family history, and social history. These are essential components of the subjective portion of building a health history for any patient (Ball et al., 2022). Even though the review of the systems is also part of health history, the subjective portion of this episodic SOAP note is sufficient to construct a list of diagnoses and differential diagnoses. However, this portion would be more sufficient with extra elements to rule in or out some differential diagnoses. Important negatives are key aspects of building health history that directs the diagnostic approach and thinking of the doctor and the nurse in a patient evaluation.
The subjective portion mentioned the presence of intermittent epigastric pain. However, I would inquire more about the presence or absence of these symptoms in relation to food intake. Food intake influence is vital in evaluating dyspepsia and upper gastrointestinal symptoms because it can exacerbate or relieve some of the symptoms. Other exacerbations and relief of this pain, such as physical activity and abdominal distention, are also useful pieces of information in this patient’s history. The history of the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is also important to exclude the role of these medications in this patient’s epigastric pain.
Objective Portion
The objective portion of this episodic SOAP note contained vital signs, heart examination, respiratory, skin, abdominal examination, and diagnostic results. The documentation is focused on signs and other objective features pertinent to the patient’s chief complaint. Most of the time, the objective aspects presented are determined by the examiners’ thought process of working up the patient. However, additional information on this patient’s initial investigations, such as a urease breath test, would be important to rule out the likelihood of peptic ulcer disease. Additional information on this patient’s general condition, such as respiratory distress, body build, and mental status, is also vital in figuring out the current general state of the patient. Additional tests such as abdominal ultrasound scans and esophagogastroduodenoscopy will save some time in the evaluation of this patient.
Diagnostic Tests
Serum electrolytes, urea, and creatinine are also baseline tests that would provide additional information on the biochemical function of the patient concerning renal and metabolism status. As aforementioned, esophagogastroduodenoscopy and abdominal ultrasound scan of the abdomen would also provide vital anatomical information on the etiology of this patient’s pain (Schill et al., 2022). A complete blood count would be essential in finding out whether there are infectious and inflammatory etiologies of this patient’s pain. Serum lipase levels will help in ruling out pancreatic disease.
Assessment
The provided differential diagnoses are relevant to the documented subjective and objective information. An abdominal aortic aneurysm is supported by the long-standing presence of symptoms and lack of response to proton pump inhibitors. This condition is life-threatening and would warrant his current emergency department admission (Shaw et al., 2023). The provided test would be essential in the evaluation of abdominal aortic aneurysms (Schill et al., 2022).
The current deterioration could also indicate a complicated peptic ulcer disease in this patient. PUD can perforate, resulting in peritonitis that would present with pain (Kuna et al., 2019). However, this pain would be generalized and cause rebound tenderness or guarding. The third assessment, pancreatitis, is also a likely diagnosis in this patient. Even though the lack of response to PPIs would suggest an etiology outside the stomach and duodenum, the role of pancreatitis in this patient’s presentation is mainly supported by the location of the pain. The radiation of the pain to the back would also suggest the presence of pancreatitis.
Verdict on the Assessment
I accept the current assessments based on the available objective and subjective information. However, additional possible diagnoses would also apply to this patient based on the provided history and physical examination. Acute cholecystitis, small intestinal obstruction, and chronic gastritis are also likely diagnoses in this patient. Small bowel obstruction in this patient is suggested by the presence of abdominal pain. However, the absence of abdominal distention or vomiting makes intestinal obstruction less likely.
The patient is a chronic tobacco user and has a positive history of alcohol intake which makes chronic gastritis more likely in this patient (Yawar et al., 2021). However, the recent acute clinical deterioration suggests an acute complication of this illness. Acute cholecystitis is also likely in this patient because this condition sometimes presents with epigastric pain, even in the absence of right upper quadrant tenderness. Therefore, this patient would benefit from an extensive workup.
Conclusion
In sum, the provided suggest that the patient has an intraabdominal illness. Perforated PUD, chronic gastritis, acute pancreatitis, acute cholecystitis, and abdominal aortic aneurysm are likely diagnoses. Therefore, additional information on the relationship between this patient’s epigastric pain to food intake and recent meditation use is essential. Additional investigations such as esophagogastroduodenoscopy, abdominal ultrasound, serum lipase level, full blood count, serum electrolytes, and urea levels should suffice further workup before definitive management.
References
Ball, J. W., Dains, J. E., Flynn, J. A., Solomon, B. S., & Stewart, R. W. (2022). Seidel’s physical examination handbook: An interprofessional approach (10th ed.). Elsevier – Health Sciences Division.
Kuna, L., Jakab, J., Smolic, R., Raguz-Lucic, N., Vcev, A., & Smolic, M. (2019). Peptic ulcer disease: A brief review of conventional therapy and herbal treatment options. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020179
Schill, C. N., Tessier, S., Longo, S., Ido, F., & Nanda, S. (2022). Differential diagnosis of multiple systemic aneurysms. Cureus, 14(10), e30043. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.30043
Shaw, P. M., Loree, J., & Gibbons, R. C. (2023). Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29262134/
Yawar, B., Marzouk, A. M., Ali, H., Ghorab, T. M., Asim, A., Bahli, Z., Abousamra, M., Diab, A., Abdulrahman, H., Asim, A. E., & Fleville, S. (2021). Seasonal variation of presentation of perforated peptic ulcer disease: An overview of patient demographics, management, and outcomes. Cureus, 13(11), e19618. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.19618
READ MORE >>
Case Study NeoplasmsCase Study NeoplasmsCase Study: Disorders of Musculoskeleta ...
Case Study Neoplasms
Case Study Neoplasms
Case Study: Disorders of Musculoskeletal Function: Trauma, Infection, Neoplasms
Marvin is a healthy, active 36-year-old who belongs to a martial arts club. Once a week he takes lessons in Judo, and on the weekends, he participates in local competitions. At his last competition, Marvin was paired with a skilled participant from another club.
His rival threw him to the mats, and as Marvin struggled, came down hard to pin him down. Marvin heard a snap, followed by instant pain in his left forearm Case Study Neoplasms. Radiographs at the local hospital confirmed he suffered a transverse fracture of the distal aspect of his left ulna.
- What are the typical signs and symptoms of a fracture? Why shortly after the injury does the pain temporarily subside?
- How does a hematoma form, and what function does it serve in the process of healing a fracture?
- Marvin was told he would be seeing a physiotherapist as his healing progressed. What are the muscular and joint changes that occur during immobilization and the ways Marvin and his physiotherapist can work to address these changes?
Cancer is a neoplasm that can grow rapidly, spread, and cause damage to the body. A malignant neoplasm is cancerous, while a metastatic neoplasm is malignantcancer that has spread to nearby or distant areas of the body.
The cause of benign neoplasm is often not known, but factors such as exposure to radiation or environmental toxins; genetics; diet; stress; inflammation; infection and local trauma or injury may be linked to the formation of these growths.
The sooner a malignant neoplasm is detected, the more effectively it can be treated, so early diagnosis is important. Many types of cancer can be cured. Treatment for other types can allow people to live for many years with cancer.
READ MORE >>
Cause and effect relationship in response to diseaseCause and effect relationshi ...
Cause and effect relationship in response to disease
Cause and effect relationship in response to disease
Apply knowledge of tissue and organ structure and function to physiologic alterations in systems and analyze the cause-and-effect relationship.
Select one of the case studies below. In your discussion be sure to include evidence of your knowledge of tissue and organ structure and function to physiologic alterations in systems and analyze the cause-and-effect relationship in response to disease.
Requirements
Make sure all of the topics in the case study have been addressed.
Cite at least three sources—journal articles, textbooks, or evidenced-based websites—to support the content.
All sources must have been written within five years (2012-2017).
Do not use .com, Wikipedia, or up-to-date, etc., for your sources.
Case Study 1
Mechanisms of Infectious Disease
Thirty-two–year-old Jason is a general laborer, who fell ill shortly after working on a job digging up old water pipes for the town he lived in. The task involved working around shallow pools of stagnant water. Ten days after the contract ended, Jason developed a fever and aching muscles.
He also had nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Jason’s friend took him to his physician who listened carefully to Jason’s history. She told him she suspected West Nile fever and ordered serological testing. Jason went home to recover and was feeling better by the end of the week.
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAY
Jason’s physician ordered serological tests. How would antibody titers assist the doctor in confirming his diagnosis?
When Jason was feeling at his worst, he had extreme malaise, vomiting, and diarrhea. What stage of the illness was he experiencing at that time? What are the physiological mechanisms that give rise to the signs and symptoms of infectious illness?
West Nile virus has a single-stranded RNA genome. How does this virus replicate? In general terms, what are the various effects viruses can have on host cells?
Case Study 2
Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Melissa is a 15-year-old high school student. Over the last week, she had been feeling tired and found it difficult to stay awake in class. By the time the weekend had arrived, she developed a sore throat that made it difficult to eat and even drink.
Melissa was too tired to get out of bed, and she said her head ached. On Monday morning, her mother took her to her doctor. Upon completing the physical exam, he told Melissa the lymph nodes were enlarged in her neck and she had a fever.
He ordered blood tests and told Melissa he thought she had mononucleosis, a viral infection requiring much bed rest.
Innate and adaptive immune defenses work collectively in destroying invasive microorganisms. What is the interaction between macrophages and T lymphocytes during the presentation of antigen?
Melissa’s illness is caused by a virus. Where are type I interferons produced, and why are they important in combating viral infections?
Humoral immunity involves the activation of B lymphocytes and production of antibodies. What are the general mechanisms of action that make antibodies a key component of an immune response?
Case Study 3
Disorders of the Immune Response
Ahmed has worked as a phlebotomist in the local hospital for the last 7 years. Last year, he began to complain of watery, nasal congestion and wheezing whenever he went to work. He suspected he was allergic to something at the hospital because his symptoms abated when he was at home over the weekends.
One day he arrived at work for the morning shift and put on his gloves. Within minutes, he went into severe respiratory distress requiring treatment in the emergency ward. It was determined at that time his allergic response was due to latex exposure.
Ahmed experienced a type I, IgE-mediated hypersensitivity response. How can this be determined by his signs and symptoms? How might another type of latex hypersensitivity reaction present?
How do T2H cells, mast cells, and eosinophils function to produce the signs and symptoms typical of a type I hypersensitivity disorder?
How is it that someone who does not come into direct contact with latex can still have a hypersensitivity response to the material? What do food allergies have to do with latex allergies?
Case Study 4
Inflammation, Tissue Repair, and Wound Healing
Carlton, a six-year-old boy, was playing on a sandy beach with his mother. He began to run along the shoreline when he stepped on the sharp edge of a shell, giving himself a deep cut on his foot. His mother washed his foot in the lake and put on his running shoe to take him home.
One day later, Carlton’s foot looked worse. The gash was red and painful. The foot was warm to touch and appeared swollen. Carlton’s mom put some gauze over the wound and prepared to take him to the local community health clinic.
What is the physiologic mechanism causing the wound to become red, hot, swollen, and painful? How is this different than the inflammatory response that might occur in an internal organ?
What are the immunologic events that are happening at the local level during Carlton’s acute inflammatory response?
Nutrition plays an important factor in wound healing. What stages of wound healing would be affected by a deficiency in vitamins A and C?
Case Study 5
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Patience is 29 years old and has been HIV positive for nine years. She has remained asymptomatic and is not taking antiretroviral medication. Recently she was at the drop-in clinic to talk to a public health nurse about having a baby through artificial insemination.
She said she had met a man who wanted to marry her and have children with her, but she was concerned about the baby contracting HIV.
Her latest blood tests indicated her CD4+ count was 380/µL. The PCR test indicated her viral load was 850. The nurse referred her to the physician to discuss antiretroviral therapy during her pregnancy.
What are the factors that increase the chance of HIV transmission from mother to infant, and how the transmission occurs?
Patience was told that after she became pregnant, she would begin HAART therapy. Describe what this therapy is and what particular antiretroviral medication would be particularly useful to her during her pregnancy. What concern is there about administering certain antiretrovirals early in the pregnancy?
Individuals with HIV are prone to contracting opportunistic infections. What are opportunistic infections and the risk factors that leave an individual with HIV particularly prone to contracting this type of illness?
Case Study 6
Blood Cells and the Hematopoietic System
Charlie is a 53-year-old man with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. His treatment has been only modestly successful in delaying the progression of the disease, and he has recently relapsed. His medical team decided to administer aggressive chemotherapy.
Knowing that the intensive treatment would have a destructive effect on Charlie’s bone marrow, they removed stem cells from his blood before the chemotherapy began. Afterward, the stem cells were returned by IV to reestablish his bone marrow function.
What are the therapeutic advantages of an autologous stem cell transplant on Charlie’s bone marrow and immune system?
Before harvesting stem cells, a cytokine growth factor is administered to the patient. What is the benefit of this procedure?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a disease involving B and T lymphocytes. What aspects of the immune response are these cells responsible for?
When considering erythrocytes, how is the body able to meet hematopoietic demand in conditions such as hemolytic anemia or blood loss?
READ MORE >>
Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson EnterprisesCase Study: Th ...
Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises
Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises
Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises
WRITING ASSESSMENT
By: Casey McNellis, Ronald Premuroso, & Robert Houmes
This writing assessment is designed to enhance your research skills using the FASB Codification and improve your graduate level writing skills. Login credentials to the FASB Codification are provided in the syllabus under Class Guidelines. Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises
ORDER COMPREHESIVE SOLUTION PAPERS
Academic writing is different from general writing. You are strongly advised to start this project early in the semester and engage the help of UMUC Writing Tutors. Every graduate accounting course offers free UMUC writing tutors Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises.
Register for a writing tutor at the beginning of the semester and submit drafts of this assignment for guidance Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises.
Upon receiving guidance from a UMUC writing tutor, improve your next draft, and resubmit your paper for additional guidance. Writing is an iterative process whereby you plan, research, write, edit, research more if needed, rewrite, edit, and rewrite until you have created a clear, concise, and correct paper Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises.
Instructions:
- Read the case study and prepare answers to the questions at the end of the case.
- APA style formatting is required..
- Approximate length of paper using APA style is 10 pages.
Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises Resources
Writing a Research Paper: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/658/01/
APA: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/section/2/10/
Developing your graduate level writing skills: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/section/1/2/
Proposed Accounting Standards Update: Simplifying the Accounting for Goodwill Impairment, by FASB; May 12, 2016: http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Document_C/DocumentPage?cid=1176168146260&acceptedDisclaimer=true
What Constitutes Graduate Level Writing; source unknown. In LEO, Content, Week 9.
1. Identify and cite the relevant topics/subtopics from the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for this case.
Average cost is $1,495; times 1.5385 equals a selling price of $2,300. The $2,300 unit selling price less $1,495 unit cost equals a gross margin of $805, which is 35 percent of selling price.
2. Identify the specific accounting issue that you believe needs to be initially addressed for JE’s consideration of goodwill with regards to both Dynamic and ZD.
3. What does the qualitative evidence from the case indicate about whether JE should perform the two-step impairment test? In your response, identify specific factors discussed in the Codification and relate them to the information provided to you in the case Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises.
4. Beyond the assessment of qualitative factors, what other evidence should be considered for the purposes of the analysis? What does this information suggest? With respect to Dynamic, what do you think is the most appropriate fair value amount to use in assessing the fair value of this reporting unit? Explain. Why is this important?
5. Based upon the information provided above, should Dynamic and ZD be combined or separated for the purposes of the goodwill analysis? Explain. Why is this important?
6. Based upon your initial analysis, do you think the $200 million goodwill balance (i.e., the $150 million for Dynamic and the $50 million for ZD) is the appropriate valuation for goodwill on the December 31, 2014 balance sheet of JE?
7. Prepare a memo detailing the issues involved, the judgments you made in connection with the authoritative literature, and your recommendation for the direction of the goodwill valuation as it relates to Dynamic and ZD (i.e., does the evidence suggest further action is required in determining the appropriate valuation of goodwill? If so, what steps need to be taken?). Case Study: The Case of Goodwill Impairment at Jackson Enterprises
READ MORE >>
Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project PaperNR451 Capstone ProjectDirections: Please ...
Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper
NR451 Capstone Project
Directions: Please choose ONE topic and its corresponding systematic review that is of most interest to you, or most relevant to your practice Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper. This systematic review will be the basis for your capstone project. Please refer to the guidelines for each milestone for more details.
Promoting breastfeeding
Sinha, B., Chowdhury, R., Sankar, M. J., Martines, J., Taneja, S., Mazumder, S., … Bhandari, N. (2015). Interventions to improve breastfeeding outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatrica, 104, 114-134.
Preventing central venous catheter-related infections
Lai, N. M., Lai, N. A., O’Riordan, E., Chaiyakunapruk, N., Taylor, J. E., & Tan, K. (2016). Skin antisepsis for reducing central venous catheter-related infections. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (7), CD010140.

Increasing health insurance coverage for vulnerable populations
Jia, L., Yuan, B., Huang, F., Lu, Y., Garner, P., & Meng, Q. (2014). Strategies for expanding health insurance coverage in vulnerable populations. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (11), 1-41. CD008194. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008194.pub3.
Chamberlain Library Permalink: http://proxy.chamberlain.edu:8080/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=mdc&AN=25425010&site=eds-live&scope=site
Preventing teen pregnancy and sexually-transmitted disease
Mason-Jones, A. J., Sinclair, D., Mathews, C., Kagee, A., Hillman, A., & Lombard, C. (2016). School-based interventions for preventing HIV, sexually transmitted infections, and pregnancy in adolescents. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (11), CD006417. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006417.pub3.
Chamberlain Library Permalink: http://proxy.chamberlain.edu:8080/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=mdc&AN=27824221&site=eds-live&scope=site
Reducing hospital readmissions
Mistiaen, P., & Poot, E. (2006). Telephone follow-up, initiated by a hospital-based health professional, for post discharge problems in patients discharged from hospital to home. Cochrane Consumers and Communication Group. (4), CD004510. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004510.pub3.
Chamberlain Library Permalink: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com.proxy.chamberlain.edu:8080/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD004510.pub3/full
Capstone Project Milestone 1: Practice Issue and Evidence Summary Worksheets
Student Name: Date:
Directions
- Refer to the guidelines for specific details on how to complete this assignment.
- Type your answers directly into the worksheets below.
- Submit to the Dropbox by the end of Week 3, Sunday at 11:59 p.m. MT.
- Post questions about this assignment to the Q & A Forum. You may also email questions to the instructor for a private response.
- Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper
Practice Issue Worksheet
What is the Practice Issue?Define the scope of the Practice Issue: What is the practice area?___ Clinical
___ Education
___ Administration___ Other (list)_________________________________
How was the practice issue identified? (check all that apply)___ Safety/risk management concerns___ Unsatisfactory patient outcomes
___ Wide variations in practice
___ Significant financial concerns
___ Difference between hospital and community practice___ Clinical practice issue is a concern
___ Procedure or process is a time waster
___ Clinical practice issue has no scientific base
__ Other:
Describe the rationale for your checked selections:What evidence must be gathered? (check all that apply)___ Literature search___ Guidelines___ Expert Opinion
___ Patient Preferences
___ Clinical Expertise___ Financial Analysis___ Standards (Regulatory, professional, community)
___ Other
Describe the rationale for your checked selections:Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper
Evidence Summary Worksheet
Directions: Please type your answers directly into the worksheet.
Describe the practice problem in your own words with reference to the identified population, setting and magnitude of the problem in measurable terms:Find a source of evidence that is a systematic review article on a nursing topic that is relevant to your practice problem. Write the complete APA reference for the systematic review article you selected:Define the search terms for your systematic review:
Identify the objectives of the article.Provide a statement of the questions being addressed in the work and how they relate to your practice issue:
Summarize (in your own words) the interventions the author(s) suggest to improve patient outcomes.Summarize the main findings by the authors of your systematic review including the strength of evidence for each main outcome. Consider the relevance to your project proposal for the Milestone 2 project paper.
Outline evidence-based solutions that you will consider for your project.Discuss any limitations to the studies performed that you believe impacts your ability to utilize the research in your project.
iCARE Paper
Assignment
Purpose
The purpose of the iCARE Paper assignment is to explore the concept of interprofessional teams and patient outcomes Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper. Nursing supportive actions of compassion, advocacy, resilience, and evidence-based practice will serve as a way to apply care concepts.
Course Outcomes
This assignment enables the student to meet the following course outcomes:
- CO 1: Applies principles of nursing, theories, and the care philosophies to self, colleagues, individuals, families, aggregates and communities throughout the healthcare system. (PO 1)
- CO 6: Plans clinical practice activities that integrate professional nursing standards in accordance with the Nursing Code of Ethics and the American Nurses’ Association (ANA) standards of practice. (PO 6)
Due Date
Submit your completed assignment by Sunday end of Week 5 by 11:59 p.m. MT.
Total Points Possible
The assignment is worth 200 points.
Preparing the Assignment
- Please review the infographic as way to guide you in getting started with your assignment: Developing an Assignment with Integrity.
- View a short tutorial with tips for completing this assignment: iCARE Paper Tutorial
- Getting Started: Interprofessional teams are part of practice trends we see developing in all aspects of care delivery. Consider you own work environment (or recent clinical setting).
- For this assignment, consider the concept of interprofessional teamwork and patient outcomes.
- Look to your current workplace as an example. (If you are not currently employed, look to a past workplace or clinical practice area.)
- Apply the components of the iCARE concept to interprofessional teams in a short paper. (Body of the paper to be 3 pages, excluding the title page and references page)
- iCARE components are:
- C ompassion
- A dvocacy
- R esilience
- E vidence-Based Practice (EBP)
- How could you contribute to the interprofessional team, the culture of your practice setting, and positive patient outcomes through nursing actions demonstrating compassion, advocacy, resilience, and evidence-based practice?
- Select one scholarly nursing article from CINAHL as a resource for your paper.
- Additional scholarly sources can be used but are optional.
- When searching in the CINAHL database, please limit your search word to one component of the paper you wish to emphasize, such as ‘Resilience’. Searching for the term iCARE will not produce the results you need.
- Elements of iCARE paper
- Title page
- Below are the headings to be used for this assignment.
- Title of your paper as the heading for the introduction (Do not use the word Introduction, just the paper title from your title page. See page 61 of the APA Manual, 7th edition for an example). Explain the type of work setting you are discussing and whether interprofessional teams are currently present. If interprofessional teams are present, indicate a team function that could be improved. If interprofessional teams are NOT present, indicate what type of team you think might be possible in the setting.
- Describe a nursing action item for each component below that could contribute to: interprofessional team support; how this might impact the culture of your unit or organization; and possible impact on patient outcomes.
- Compassion
- Advocacy
- Resilience
- Evidence-Based Practice
- Summary: Include a summary statement of how iCARE components can support interprofessional teams and patient outcomes. Address how you may be able to influence this process of support for interprofessional teams overall in your unit or organization.
- References: List any references used in APA format.
- Getting Started: Interprofessional teams are part of practice trends we see developing in all aspects of care delivery. Consider you own work environment (or recent clinical setting).
Templates
The prepared paper template is RECOMMENDED for this assignment.
iCare Assignment Template. – APA 7th edition
Only the APA 7th edition is to be used in this assignment.
Best Practices
- Please use your browser’s File setting to save or print this page.
- The template provided is recommended.
- Spell check for spelling and grammar errors prior to final submission.
- Use the rubric as a final check prior to submission to ensure all content is clearly addressed.
- Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper
Scholarly Sources and Citations
- Use APA format for citations and references.
- Please paraphrase throughout. One short quote is permitted.
- Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper
**Academic Integrity**
As detailed in the Simple Syllabus, all required Chamberlain papers, discussions or other written learning activities are subject to submission for detection of plagiarism to Turnitin ® or other anti-plagiarism software. Remember, Chamberlain’s philosophy is Integrity Matters so please use all resources within your course and your instructor if you have any questions or need assistance with this assignment.
Chamberlain College of Nursing values honesty and integrity. All students should be aware of the Academic Integrity policy and follow it in all discussions and assignments.
By submitting this assignment, I pledge on my honor that all content contained is my own original work except as quoted and cited appropriately. I have not received any unauthorized assistance on this assignment.
iCARE Paper Example
The care management specialty pays attention to the coordination of care and effective and efficient utilization of resources to offer patients with chronic illnesses the highest quality of care during their stay in the hospital. Educating the patients, advocating for their wellness, and communicating clearly are vital to ensure their health outcomes are enhanced in the long run. It necessitates employing an interdisciplinary team with workers from other fields to ensure patients receive holistic care that suits their needs.
To ensure that this existing interdisciplinary team offers better healthcare, it is essential to employ open communication and availing of information to the team members on time. The application of resilience and compassion skills when dealing with these patients is essential to implementing practice based on scientific evidence. Despite these valuable interventions in place to ensure that patients receive the highest quality of care, the healthcare sector still faces challenges that hinder progress, requiring novel solutions.
Compassion
Compassion helps healthcare workers show kindness and understanding of patients and their loved ones, which is essential in achieving high-quality health outcomes. Forging supportive relationships based on trust has helped increase satisfaction and boost the best customer experience and entails a good show of compassion from the healthcare workers (Straughair & Machin, 2020). Compassion ensures clients receive social, psychological, physical, and emotional needs, thus promoting holistic care. To encourage compassion, an interprofessional team should ensure that the patient and family are involved in the client’s care.
The team can provide essential information about the client’s health status and involve them in decision-making about any procedures the patient will likely undergo. The team must seek informed consent from the patient or their family members if they cannot make sound decisions independently. The patient and the family will ultimately increase their trust in the interdisciplinary team and heed the interventions formulated by the team. A safety culture is forged when patients and families are involved in their care, which can increase the organization’s reputation (Son?ur et al., 2018).
Advocacy
Healthcare workers can enhance advocacy by understanding patients’ unique needs, values, and beliefs. Advocacy involves the healthcare workers standing by what the patients believe is right for them in their absence and ensuring their voice is heard during decision-making. Through advocacy, the patient’s autonomy is respected through a third party, the nurse overseeing the care of the patients. The nurse can communicate openly with the client and present them with facts so that they can apply them in making decisions, which the nurse ensures are considered by other interdisciplinary teams when tailoring interventions (Abbasinia et al., 2019).
Nurses can aid in fostering a culture of patient-centered care by making the advocacy of patients a top priority and promoting teamwork among healthcare professionals. Better patient experience and clinical outcomes may result from this shift in attitude on the healthcare team. Evidence suggests that a patient-centered culture helps to decrease the number of hospitalizations and a general improvement in the quality of care of all patients.
Resilience
Promoting effective collaboration and open communication channels among the different interdisciplinary teams in the hospital can promote resilience. Resilient healthcare personnel can deal with the stresses of their jobs without letting them affect their health or performance. Resilience is the capacity to deal with hardship while providing excellent patient care. Heavy workloads, extended shift hours, psychological demands, and experiencing traumatic events entail pressures that healthcare employees experience (Odom-Forren, 2020). Because of their resilience, they can overcome these challenges and continue providing excellent patient treatment.
Resilient healthcare providers are better equipped to deal with difficult situations, keep a positive attitude, and communicate effectively with patients and their families (Odom-Forren, 2020). They are not likely to suffer from burnout, which is associated with dissatisfaction with one’s work and an increased likelihood of making mistakes in patient care. Resilience can help keep workers motivated to provide high-quality healthcare to their patients, devoid of errors, which can help achieve the organization’s mission and vision.
Evidence-Based Practice
Carrying out regular interdepartmental sessions to enlighten the healthcare workers about relevant changes in guidelines in managing healthcare conditions and new evidence that supports those changes can help foster evidence-based practice. Along with other medical experts, nurses can learn from one another at these conferences and improve their ability to give patients evidence-based care. Encouraging an approach based on scientific evidence, applied by interprofessional teams, the organization’s culture can value the inception of interventions based on the current evidence and research in informing patient care (Son?ur et al., 2018).
The healthcare outcomes are likely to improve since interventions backed up with credible scientific findings can help enhance the overall quality of care and complications experienced by patients and promote increased patient satisfaction. The organization’s reputation improves, and reimbursements are likely to increase. When workers apply evidence-based interventions and see improved patient outcomes, they can become highly motivated and will likely work for longer in the organization, decreasing employee turnover.
Summary
Employment of the iCARE components can help increase patient satisfaction, enhance patient outcomes, and promote collaboration through interdisciplinary teams. These components can help promote a patient-centered culture that ensures patients are involved in their care and that they make their own decisions. They are also empowered to partake in self-care, which has been shown to increase the overall quality of care and satisfaction. Ensuring that the patient’s beliefs, values, and attitudes are considered in decision-making ensures that they accept the interventions employed by the healthcare teams. Nurses can influence the adoption of interdisciplinary teams in the organization by advocating for the adoption of iCARE and providing evidence on how they can be essential in improving the achievement of organizational goals.
References
Abbasinia, M., Ahmadi, F., & Kazemnejad, A. (2019). Patient advocacy in nursing: A concept analysis. Nursing Ethics, 27(1), 141–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733019832950
Odom-Forren, J. (2020). Nursing resilience in the world of COVID-19. Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing, 35(6), 555–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jopan.2020.10.005
Son?ur, C., Özer, Gün, Ç., & Top, M. (2018). Patient safety culture, evidence-based practice and performance in nursing. Systemic Practice & Action Research, 31(4), 359–374. https://doi-org.chamberlainuniversity.idm.oclc.org/10.1007/s11213-017-9430-y
Straughair, C., & Machin, A. (2021). Compassion in nursing: exploring the perceptions of students and academics. Nursing standard (Royal College of Nursing (Great Britain): 1987), 36(7), 45–50. https://doi.org/10.7748/ns.2021.e11720
Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper Rubric
Week 5 iCARE Paper Grading RubricWeek 5 iCARE Paper Grading RubricCriteriaRatingsPtsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Introduction
The type of work setting and interprofessional team features are described (improvement or type of team).25 pts
Introduction thoroughly describes the work setting and features of the interprofessional team.22 pts
Introduction describes the work setting and features of the interprofessional team.20 pts
One element from the first column is missing or lacks detail.10 pts
Two elements from the first column are missing and lack detail.0 pts
The introduction is missing.Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper25 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Compassion
Nursing action related to compassion is described in support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.25 pts
The nursing action related to compassion was clearly identified and support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes were thoroughly explained.22 pts
The nursing action related to compassion was identified and satisfactorily supported the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.20 pts
The nursing action related to compassion was identified and one of the elements of support from the first column were missing or lacked detail.10 pts
The nursing action related to compassion lacked more than two elements of support or lacked detail.0 pts
No Marks25 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Advocacy
Nursing action related to advocacy is described in support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.25 pts
The nursing action related to advocacy was identified and support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes were thoroughly explained.22 pts
The nursing action related to advocacy was identified and satisfactorily supported the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.20 pts
The nursing related to advocacy was identified and one of the elements of support from the first column were missing or lacked detail.10 pts
The nursing action related to advocacy lacked more than two elements of support or lacked detail.0 pts
The nursing action and support elements were missing.25 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Resilience
Nursing action related to resilience is described in support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.25 pts
The nursing action related to resilience was identified and support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes were thoroughly explained.22 pts
The nursing action related to resilience was identified and satisfactorily supported the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.20 pts
The nursing action related to resilience was identified and one of the elements of support from the first column were missing or lacked detail.10 pts
The nursing action related to resiliency lacked more than two elements of support or lacked detail.0 pts
The nursing action and support elements were missing.25 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Evidence-Based Practice
Nursing action related to EBP is described in support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.25 pts
The nursing action related to EBP was identified and support of the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes were thoroughly explained.22 pts
The nursing action related to EBP was identified and satisfactorily supported the interprofessional team, the culture of the unit, and patient outcomes.20 pts
The nursing action related to EBP was identified and one of the elements of support from the first column were missing or lacked detail.10 pts
The nursing action related to EBP was not sufficiently identified or one of the elements of support from the first column were missing or lacked detail.0 pts
The nursing action and support elements were missing.25 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Summary
Explain how nursing actions of the iCARE components can support interprofessional teams and patient outcomes. Address how you can influence support for interprofessional teams on your unit or area of practice.35 pts
Key points regarding nursing actions and support for interprofessional teams and patient outcomes; and, nursing supportive influence are thoroughly described.31 pts
Most key points regarding nursing actions and support for interprofessional teams and patient outcomes; and, nursing supportive influence are described.28 pts
Some key points regarding nursing actions and support for interprofessional teams and patient outcomes; and, nursing supportive influence are described13 pts
Summary lacks details of key points.0 pts
Summary is missing.35 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Mechanics and Organization
The discussion is well organized and logical. The structure is clear and compelling to the reader. Paragraphs are linked together logically, and main ideas stand out20 pts
Excellent mechanics and organization with minimal errors of the following: Well organized and logical, correct grammar, punctuation, and spelling, professional wording is used, uses complete sentences, paragraphs are linked together logically, and main ideas expressed clearly.18 pts
Good mechanics and organization considering the elements listed in the column A. Few errors noted.16 pts
Fair mechanics and organization considering the elements listed in the column A. Some errors noted.8 pts
Poor mechanics and organization considering the elements listed in the column A. Many errors noted.0 pts
Very poor mechanics and organization considering the elements listed in the column A such that it is difficult to follow or understand.20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome APA
APA format is used throughout.Chamberlain NR451 Capstone Project Paper20 pts
Excellent APA formatting with minimal errors of the following: All sources cited in the text -all references listed on the reference page using basics of APA format -title page in general APA format -headings present and follow APA format -12-point font, double spaced, 1 inch margins, paragraphs indented -used only one short quote and body of the paper is approximately 3 pages18 pts
Good formatting considering the elements listed in column A.16 pts
Fair formatting considering the elements listed in column A. Some APA errors noted.8 pts
Poor formatting considering the elements listed in column A. Many APA errors noted.0 pts
Very poor formatting such that paper is difficult to read. Numerous APA errors noted.20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Use of CINAHL article as Required Source from CCN Library
0 pts
0 points deductedUsed CINAHL article from CCN Library0 pts
20 points (10%) deductedRequired article source of CINAHL not used resulting in point deduction0 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Late Deduction
0 pts
0 points deductedSubmitted on time0 pts
Not submitted on time – Points deducted1 day late = 10 deduction; 2 days late = 20 deduction; 3 days late = 30 deduction; 4 days late = 40 deduction; 5 days late = 50 deduction; 6 days late = 60 deduction; 7 days late = 70 deduction; Score of 0 if more than 7 days late0 ptsTotal Points: 200READ MORE >>
Chamberlain NR703 Week 7 AssignmentChamberlain NR703 Week 7 AssignmentProfession ...
Chamberlain NR703 Week 7 Assignment
Chamberlain NR703 Week 7 Assignment
Professional DNP Leadership Capacity Assignment NR703
Purpose
NOTE: This assignment must use the provided Paper Template which is found in this Link (Word doc): Week 7 Assignment Paper Template.
The purpose of this assignment is to demonstrate your leadership capacity to manage a practice change project. You will create a collective manuscript that incorporates the revised Week 2 and Week 5 assignments with an additional section that you will create this week.
This assignment will allow for the assimilation of professional leadership competencies in project management as a DNP-prepared nurse. Assignment content supports professional formation, communication, and dissemination skills relevant to the DNP-prepared nurse.
Please note that this is the third part of a 3-part assignment submitted in Weeks 2, 5, and 7. You have received feedback from your course faculty on the Week 2 and Week 5 assignments, which you should use to revise and prepare the Week 7 assignment.
NOTE: All NR703 assignments and their requirements should be discussed in relation to your proposed or hypothetical DNP practicum project.
Also Read:
NR703 Week 8 Reflection on Learning and Practice Readiness Discussion
Instructions
Use the provided Week 7 Assignment Paper Template and include the following:
- Introduction: The organizing introduction is the first paragraph that does the following:
- Introduce the paper’s topic and establishes its importance.
- Present a clear purpose statement.
- Create a brief overview (outline statement) for the combined paper using the three primary Level 1 headings.
- Integrate the Week 2 corrected content under the first Level 1 heading, “Organizational Needs Assessment.”
- Don’t forget to include the discussions of Table 1 (Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification) and Table 2 (Johns Hopkins Individual Evidence Summary Tool). Both tables must be referred to in the paper’s content.
- Include the required level 2 headings (as they are on the template):Practice Gap
- Problem
- Practice Gap
- Practice Question
- Integrate the Week 5 corrected assignment content under the second Level 1 heading, “Leading the Practice Change Project,” using the following level 2 headings (Note: level 3 headings for sub-topics are recommended):
- Interprofessional Collaboration in Leading Project Teams
- Communicating Comportment in Project Management
- Leadership Ethics
- Create the content to place under the third Level 1 heading, “Leading Practice Change Teams with Innovation and Effective Management,” using the following level 2 headings:
- Leading Through Innovation
- Integrating Leadership and Management Models
- Managing Materials and Human Resources
- Conclusion
- Recap the paper’s purpose statement and brief overview (outline statement) for the combined paper using the three level 1 headings (don’t include “conclusion”).
- Draw major conclusions from the body of your paper.
- Summarize the paper’s relevance to the practice change project.
- References (minimum of 4 scholarly, peer-reviewed sources)
- Create a reference page.
- Include the references from the first two papers that you have used in this paper if they are still used.
- Ensure each reference has a matching citation.
- Support your paper by using evidence from at least four (4) scholarly peer-reviewed journal article sources (preferably research or systematic reviews) that are retrieved from the Chamberlain library databases. Do not use the internet, textbooks, government sources, or organizational websites for these four sources in this assignment. However, you may use other gray materials for additional sources if you need them.
- Attach the revised Table 1 (Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification) and Table 2 (Johns Hopkins Individual Evidence Summary Tool) from the Week 2 assignment as displayed on the Week 7 Assignment Template
Review the rubric for the grading criteria.
APA Guidelines

Use the current Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA Manual) and the Chamberlain Guidelines for Writing Professional Papers: Graduate Programs (located in the APA Basics section of the Writing Center) to complete this assignment. Follow these guidelines when completing each component. Contact your course faculty if you have questions.
- Use the NR703 Week 7 Assignment Template provided to insert your content for this assignment.
- Link (Word doc): Week 7 Assignment Paper Template.
- Personalize the title page by adding your name and the session month and year of the course where indicated.
- The title is already provided for you in the template.
- Turn on Grammarly to check the correctness of the grammar and punctuation as you write. (Note: if you have not already done so, please download the free version at Grammarly.com before the construction of the assignment.)
- Note: Because this assignment builds on the materials used in the Weeks 2 and 5 assignments as well as several discussions, similarities are expected; therefore, Turnitin will not be routinely used in this cumulative assignment. However, papers may be reviewed in Turnitin if the instructor deems it necessary.
- Use the following prescribed Level 1 and Level 2 headings, which are already provided in the template, for this paper (level 3 headings are encouraged where needed):
- Organizational Needs Assessment
- Problem
- Practice Gap
- Practice Question
- Leading the Practice Change Project
- Interprofessional Collaboration in Leading Project Teams
- Communicating Comportment in Project Management
- Leadership Ethics
- Leading Practice Change Teams with Innovation and Effective Management
- Leading Through Innovation
- Integrating Leadership and Management Models
- Managing Materials and Human Resources
- Conclusion
- Organizational Needs Assessment
Writing Requirements (APA format)
- Length: 8-12 pages for accumulated paper (not including the title page, references page, or tables)
- Use the Week 7 Assignment Paper Template that is formatted with the following APA conventions
- 1-inch margins
- Double-spaced pages
- 12-point Times New Roman
- Headings & subheadings
- Title page
- Reference page
- Table 1 and Table 2
- In-text citations
- Standard English usage and mechanics
- CARE Plan paragraph development structure
- Revisions based on course faculty feedback from Week 2 and 5 Assignments
Program Competencies
This assignment enables the student to meet the following program competences:
- Applies organizational and system leadership skills to affect systemic changes in corporate culture and to promote continuous improvement in clinical outcomes. (PO 6)
- Appraises current information systems and technologies to improve health care. (POs 6, 7)
- Creates a supportive organizational culture for flourishing collaborative teams to facilitate clinical disease prevention and promote population health at all system levels. (PO 8)
Course Outcomes
This assignment enables the student to meet the following course outcomes:
- Compare and contrast theories of organizational behavior and leadership. (PCs 2, 4; PO6)
- Investigate the role of advanced nursing practice in innovation and transformation to propose solutions impacting healthcare systems. (PCs 2, 4; PO 6)
- Differentiate attributes of effective leaders and followers in influencing healthcare. (PCs 2, 4; PO 6)
- Assimilate attributes for interprofessional collaboration across healthcare settings. (PC 6; PO 8)
- Formulate selected strategies for leadership and influence across healthcare systems. (PC 6; PO 8)
Due Date
- By 11:59 p.m. MT on Sunday
- Late Assignment Policy applies
Student Learning Resources
Click on the following tabs to view the resources for this week.
- Required Textbooks
- Required Articles
- Additional Resources

Broome, M. E., & Marshall, E. S. (2021). Transformational leadership in nursing: From expert clinician to influential leader (3rd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
- Read Chapter 9
White, K., Dudley-Brown, S., & Terhaar, M. (2021). Translation of evidence into nursing and healthcare (3rd ed.). Springer Publishing Company.
- Read Chapter 11
Learning Success Strategies
- Reflect on previous discussions from NR715 and NR716 about the Global Burden of Disease (GBD), including pandemic responses, and consider how you, as a DNP-prepared nurse, will manage the problem in a practice setting.
- Develop your ideas and thoughts through the interactive discussion. Review the discussion guidelines and rubric to optimize your performance.
- You have access to a variety of resources to support your success. Click on the DNP Resources tab on the home page to access program and project resources.
- Your course faculty is here to support your learning journey. Reach out for guidance with study strategies, time management, and course-related questions.
Interacting with Feedback
Each week your course faculty will provide feedback in the rubric and on any assignment you have submitted. Take a moment to review the following video on how to view rubric feedback in Canvas:
- Link (video): Looking at FeedbackLinks to an external site.(2:26)
Review the following video on how to accept/reject track changes when viewing course faculty feedback on your assignment:
- Link (video): Word: Track Changes and Comments(4:19)
W7 Chamberlain NR703 Week 7 Assignment Grading Rubric
W7 Assignment Grading RubricCriteriaRatingsPtsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome IntroductionRequirements:
1. Introduce the paper’s topic and establish its importance.
2. Present a clear purpose statement.
3. Create a brief overview for the combined paper using the three primary Level 1 headings.
Includes all requirements and provides an in-depth introduction.
9 ptsIncludes 2 requirements and/or provides a sufficient introduction.
8 ptsIncludes 1 requirement and/or provides a partial introduction.
0 ptsProvides an undeveloped introduction.
10 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Organizational Needs Assessment: Problem: Using the information that you gathered on the Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification (Table 1), describe the practice problem.Requirements:
1. Describe a specific location (hospital unit, community health clinic, surgical suite, primary care practice).
2. Identify the key stakeholders (decision-makers).
3. Relate the practice problem identified by the stakeholders.
Includes all requirements and provides an in-depth discussion in the assessment of the practice problem.
18 ptsIncludes at least 2 requirements and/or provides a sufficient description of the problem.
16 ptsIncludes at least 1 requirement and/or provides a partial description of the problem.
0 ptsProvides an undeveloped description of the problem.
20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice GapOrganizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap
Requirements:
1. In 1-2 organized paragraphs, summarize the Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification (Table 1).
2. Add the revised Table 1 to the paper after the reference list (use the Assignment Template). Table 1 must be referred to in this section’s content.
3. Add the revised Table 2 to the paper after the reference list (use the Assignment Template). Table 2 sources must be included in the reference list and cited in the paper.
20 ptsIncludes all requirements and provides an in-depth summary of the Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification
18 ptsIncludes 2 requirements and/or provides a sufficient summary of the Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification.
16 ptsIncludes 1 requirement and/or provides a partial summary of the Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification.
0 ptsMissing both tables and/or provides an undeveloped or no summary of the Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Gap Identification.
20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Organizational Needs Assessment: Practice Question-Define and briefly explain the project’s intended population, evidence-based intervention, and measurable outcomes (PICOT).Requirements:
1. Population. Describe the specific characteristics of the population.
2. Intervention. Based on the evidence in the Johns Hopkins Individual Evidence Summary Tool (Table 2) initiated in previous courses, describe your evidence for an evidence-based intervention.
3. Comparison: State as “compared to current practice” for the purposes of this assignment.
4. Outcome. Create and explain specific outcome measurements based on the current evidence collected in the Johns Hopkins Individual Evidence Summary Tool (attached as Table 2).
5. State the Practice Question.
Includes all requirements and provides an in-depth summary of the practice question.
18 ptsIncludes no fewer than 5 of the requirements and provides a sufficient summary of the practice question.
16 ptsIncludes no fewer than 4 of the requirements and provides a partial summary of the practice question.
0 ptsIncludes fewer than 4 of the requirements and/or provides an undeveloped summary of the practice question.
20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Leading the Practice Change Project: Interprofessional Collaboration in Leading Project TeamsRequirements:
Create an approach to implementing the practice change project with an interprofessional team, including a description of how you will manage the following challenges:
1. Creating a climate of mutual respect and shared values.
2. Facilitating team roles and flexibility to perform effectively.
Includes both requirements and provides an in-depth analysis of implementing the project with an interprofessional team.
18 ptsIncludes both requirements and provides a sufficient analysis of implementing the project with an interprofessional team.
16 ptsIncludes at least 1 requirement and/or provides a partial analysis of implementing the project with an interprofessional team.
0 ptsProvides an undeveloped analysis of implementing the project with an interprofessional team.
20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Leading the Practice Change Project: Communication Comportment in Project ManagementRequirements:
Create a guideline for your professional communication to serve you in the practice change project and future roles. Include the following:
1. Verbal and non-verbal communication competencies at a doctoral level:
i) Communicating leadership comportment
ii) Creating alignment of verbal and nonverbal messages
2. Written professional communication:
i) Writing with a leadership tone and style
ii) Using standard English
iii) Creating summary and synthesis in writing
Includes all 5 components and provides an in-depth summary of professional communication.
18 ptsIncludes at least 4 of the 5 components and/or provides a sufficient summary of professional communication.
16 ptsIncludes at least 3 of the 5 components and/or provides a partial summary of professional communication.
0 ptsIncludes fewer than 3 of the 5 components and/or provides an undeveloped summary of professional communication.
20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Leading the Practice Change Project: Leadership EthicsRequirements: Discuss how you will create a consistent image of ethical comportment, including consideration of the following:
1. Balance an Ethic of Justice with an Ethic of Care in your leadership style.
2. Create a conflict resolution approach for the project team management of issues.
3. Lead social justice change within the project environment.
Includes all requirements and provides an in-depth discussion of leadership ethics.
18 ptsIncludes at least 2 requirements and/or provides a sufficient discussion of leadership ethics.
16 ptsIncludes at least 1 requirement and/or provides a partial discussion of leadership ethics.
0 ptsProvides an undeveloped discussion of leadership ethics.
20 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Leading Practice Change Teams with Innovation and Effective ManagementRequirements:
1. Leading Through Innovation.
2. Integrating Leadership and Management Models.
3. Managing Materials and Human Resources.
40 ptsIncludes all requirements and provides an in-depth discussion of leading practice change teams with innovation and effective management.
36 ptsIncludes at least 2 requirements and/or provides a sufficient discussion of leading practice change teams with innovation and effective management.
32 ptsIncludes at least 1 requirement and/or provides a partial discussion of leading practice change teams with innovation and effective management.
0 ptsProvides an undeveloped discussion of leading practice change teams with innovation and effective management.
40 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome ConclusionRequirements:
1. Recap the paper’s purpose statement and brief overview criteria.
2. Draw major conclusions from the body of your paper.
3. Summarize the paper’s relevance to the practice change project.
Includes all requirements and provides an in-depth summary in the conclusion.
9 ptsIncludes at least 2 requirements and/or provides a sufficient summary in the conclusion.
8 ptsIncludes at least 1 requirement and/or provides a partial summary in the conclusion.
0 ptsProvides an undeveloped summary in the conclusion.
10 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome ReferencesRequirements:
1. Create the reference page that includes the references in Table 2.
2. Ensure each reference has a matching citation, & reference and citations are in the current APA style.
3. Support your discussion by using evidence from at least four (4) scholarly peer-reviewed journal article sources.
10 ptsIncludes all requirements of the reference section, at least three scholarly references with matching citations, and the reference page is formatted without errors.
9 ptsIncludes at least 2 requirements for the reference section and/or the reference page is formatted with 1-2 error types (patterns).
8 ptsIncludes 1 requirement for the references and/or the reference page is formatted with 3-5 error types (patterns).
0 ptsIncludes no requirements for the reference section and/or the reference page is formatted with 6 or more error types (patterns).
10 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome APA Style and StandardsRequirements:
1. Use the prescribed level 1 and level 2 headings, and add level 3 headings as appropriate to your content.
2. APA style is maintained in the template, and the assignment template is used.
3. Paper is 8-12 pages in length, excluding the title page, reference pages, and tables.
Includes all requirements of APA style.
27 ptsIncludes 2 requirements of APA style.
22 ptsIncludes 1 requirement of APA style.
0 ptsIncludes no requirement of APA style that conforms to the current APA manual.
30 ptsThis criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Clarity of WritingRequirements:
1. Standard English grammar, punctuation, spelling, & sentence structure conform to guidelines in the APA manual.
2. APA style/ mechanics/ grammar & Week 2 & 5 content corrections/ revisions were completed based on faculty feedback.
3. Organized and logical presentation of ideas in paragraphs (CARE Plan), sentences, and phrases.
Includes all requirements and demonstrates an in-depth clarity of writing.
27 ptsIncludes all requirements and demonstrates a sufficient clarity of writing.
22 ptsIncludes no fewer than 2 requirements and/or demonstrates partial clarity of writing.
0 ptsIncludes 1 or fewer requirements and/or demonstrates an undeveloped clarity of writing.
30 ptsTotal Points: 250PreviousNext
READ MORE >>
Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring PresentationWeek 7 Assignm ...
Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation
Week 7 Assignment: Theoretical Framework to Support Evidence-based Practice: PowerPoint Presentation
Guidelines with Scoring Rubric
Purpose
Master’s prepared nurses actively engage in the process of translating nursing knowledge into practice, thereby establishing evidence-based approaches within the discipline Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation. Throughout this process, a theoretical framework provides a meaningful context to guide and support the evidence-based practice. The purpose of this assignment is to identify a theory or model which can be used as a framework for a future evidence-based project within the MSN program.

Also Read:
NR501 Week 9 Assignment
Course Outcomes
Through this assessment, the student will meet the following Course Outcomes:
- Apply nursing theory as a framework to guide the translation of knowledge and implementation of evidence-based practice in future professional settings. (CO #2)
- Analyze theories from nursing and relevant fields with respect to the components, relationships among the components, and application to advanced nursing practice. (CO#4)
- Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation
Total Points Possible
This assessment is worth 100 points.
Due Date
Submit your file(s) by 11:59 p.m. MT Sunday at the end of Week 7.
Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation Requirements
Criteria for Content
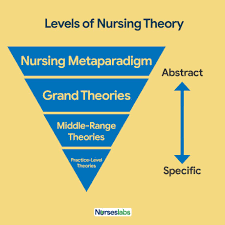
Review literature regarding issues or concerns within your selected area of advanced practice nursing Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation.
Select a theory or model which is relevant to your selected area of advanced practice nursing and would offer a meaningful context for evidence-based practice surrounding the issue or concern which you identified.
- In a PowerPoint Presentation, address the following.
- Introduction to the presentation
- Identify and describe a theory or model, and explain its relevance to the selected area of advanced practice
- Describe an issue or concern regarding the selected area of advanced practice, and explain its impact on health care outcomes
- Explain how the theory or model can be used as a framework to guide evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern, and discuss the unique insight or perspective offered through the application of this theory or model.
- Conclusion to the presentation
- References
Submission Requirements
- Application: Use Microsoft Word 2013™ to create the PowerPoint presentation.
- Length: The PowerPoint presentation must be 7 total slides (excluding title and reference slides).
- Speaker notes are used and include in-text citations when applicable.
- A minimum of three (3) scholarly literature sources must be used.
- Submission: Submit your files.
- Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation
Best Practices in Preparing the Presentation
The following are best practices in preparing this presentation:
- Review directions thoroughly.
- Follow submission requirements.
- Make sure all elements on the grading rubric are included.
- Rules of grammar, spelling, word usage, and punctuation are followed and consistent with formal, scientific writing.
- Review the Creating a Professional Presentation located in Course Resources.
- Ideas and information that come from scholarly literature must be cited and referenced correctly.
- A minimum of three (3) scholarly literature sources must be used.
- Abide by CCN academic integrity policy.
- Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation
Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation References
- Carper, B.A. (1978). Fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing. Retrieved 8 September 2019 from
- https://www.google.co.ke/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/8871/eb88fb06168bb31e20e9c54e57920e575a47.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwje0JrqscHkAhVClFwKHYXzAgsQFjAQegQICRAB&usg=AOvVaw0CEuuz-eqnIwVMqcmUI55E
- Haswell, N. (2019). The four ethical principles and their application in aesthetic practice. Journal of Aesthetic Nursing, 8(4), 177-179. Doi: 10.12968/joan.2019.8.4.177
- Schmidt, L.A., Nelson, D. & Godfrey, L. (2003). A clinical ladder program based on Carper’s fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing. JONA, 33(3), 146-152. Doi: 10.1097/00005110-200303000-00005
- Quaglietti, S., Blum, L. & Ellis, V. (2004). The role of the adult nurse practitioner in palliative care. Journal of Hospice and Palliative Nursing, 6(4), 209-214. Doi: 10.1097/00129191-200410000-00009
Grading Criteria
CategoryPoints%DescriptionIntroduction(1 slide)1010%Introduction includes general information on what will be presented. Identify sections of the PowerPoint presentation.Identification of Theory or Model (2 slides)2020%Identification and overview of one theory or model. Explanation of its relevance to the selected area of advanced practice nursing.Provide speaker notes. Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions made.Issue or Concern in selected area of Advanced Practice Nursing(1 slide)2020%Describe one specific issue or concern within the selected area of advanced practice nursing. Explanation of the impact of this issue or concern on health outcomes. Provide speaker notes. Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which validate the importance of the issue or concern.Theory as Framework for Evidence-based Practice (2 slides)2020%Explain how the theory or model can serve as a framework to support evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern. Discuss the unique insight or perspective offered through the application of this theory or model. Provide speaker notes. Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions which you present.Conclusion (1 slide)1515%Summarize key information presented in PowerPoint presentation. Provide speaker notes.APA Format55%Ideas and information that come from scholarly sources must be cited and referenced correctly. In-text and parenthetical citations must be used and may be provided on the slide or within the speaker notes. Slides, speaker notes, and references are consistent with APA 6th edition format. A minimum of three (3) scholarly references are used.Presentation of Slides55%PowerPoint presentation includes title slide, 7 content slides, reference slide(s). Presentation of slides are professional in appearance and tone. Balance among space, words and graphics, and color is effective.Writing Mechanics55%Rules of grammar, spelling, word usage, and punctuation are followed and consistent with formal written work as found in the 6th edition of the APA manual.Total100100%A quality assignment will meet or exceed all the above requirements.Assessment CriteriaExceptional(100%)Outstanding or highest level of performanceExceeds(88%)Very good or high level of performanceMeets(80%)Competent or satisfactory level of performanceNeeds Improvement(38%)Poor or failing level of performanceDeveloping(0)Unsatisfactory level of performanceContent Possible Points = 85 PointsIntroduction 10 Points 0 PointsPresentation of information is concise and includes the following element:· Identification of sections of the presentation Presentation of information is missing the following:· Identification of sections of the presentationIdentification of Theory or Model20 Points18 Points16 Points8 Points0 PointsPresentation of information is comprehensive and concise and includes all of the following elements:· Identifies one theory or model· Explains the relevance of the theory or model to the selected area of advanced practice nursing· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions made.
Presentation of information is superficial in places and includes all of the following elements:· Identifies one theory or model· Explains the relevance of the theory or model to the selected area of advanced practice nursing
· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions made.
Presentation of information is minimally demonstrated and includes all of the following elements:· Identifies one theory or model· Explains the relevance of the theory or model to the selected area of advanced practice nursing
· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions made.
Presentation of information in one of the following elements fails to meet expectations or is missing the following:· Identifies one theory or model· Explains the relevance of the theory or model to the selected area of advanced practice nursing
· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions made.
Presentation of information in two or more following elements fail to meet expectations or are missing the following:· Identifies one theory or model· Explains the relevance of the theory or model to the selected area of advanced practice nursing· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions made.
Issue or Concern in selected area of Advanced Practice Nursing 20 Points18 Points16 Points8 Points0 PointsPresentation of information is comprehensive and concise and includes all of the following elements:· Describes one specific issue or concern within the selected area of advanced practice nursing.· Provides speaker notes· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which validate the importance of the issue or concern.
Presentation of information is superficial in places and includes all of the following elements:· Describes one specific issue or concern within the selected area of advanced practice nursing.· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which validate the importance of the issue or concern.
Presentation of information is minimally demonstrated and includes all of the following elements:· Describes one specific issue or concern within the selected area of advanced practice nursing.· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which validate the importance of the issue or concern.
Presentation of information in one of the following elements fails to meet expectations or is missing the following:· Describes one specific issue or concern within the selected area of advanced practice nursing.· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which validate the importance of the issue or concern.
Presentation of information in two or more of the following elements fail to meet expectations or are missing the following:· Describes one specific issue or concern within the selected area of advanced practice nursing.· Provides speaker notes· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which validate the importance of the issue or concern.
Theory as Framework for Evidence-based Practice 20 Points18 Points16 Points8 Points0 PointsPresentation of information is comprehensive and concise and includes all of the following elements:· Explains how the theory or model can serve as a framework to support evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern.· Provides speaker notes· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions which are presented.
Presentation of information is superficial in places and includes all of the following elements:· Explains how the theory or model can serve as a framework to support evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern.· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions which are presented.
Presentation of information is minimally demonstrated and includes all of the following elements:· Explains how the theory or model can serve as a framework to support evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern.· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions which are presented.
Presentation of information in one of the following elements fails to meet expectations or is missing the following:· Explains how the theory or model can serve as a framework to support evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern.
· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions which are presented.
Presentation of information in two or more of the following elements fail to meet expectations or are missing the following:· Explains how the theory or model can serve as a framework to support evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern.· Provides speaker notes
· Speaker notes and/or slides include citations from scholarly nursing literature which support the assertions which are presented.
Conclusion 15 Points 12 Points 0 PointsPresentation of information is comprehensive and concise and includes the following element:· Summarizes key information presented in PowerPoint presentation· Provides speaker notes Presentation of information is minimally demonstrated in the following element:· Summarizes key information presented in PowerPoint presentation· Provides speaker notes Presentation of information in the following element is missing:· Summarizes key information presented in PowerPoint presentation· Provides speaker notesContent Subtotal ___ /85 pointsFormat Possible Points = 15 PointsAPA Format5 Points4 Points3 Points2 Points0 PointsAPA guidelines, as per the 6th edition of the manual, are demonstrated for the following:· In-text citations are used and provided on the slide or within the speaker notes.· Slides, speaker notes, and references are consistent with APA 6th edition format.One deduction for each type of APA format error.
0 to 1 APA error is present
APA guidelines, as per the 6th edition of the manual, are demonstrated for the following:· In-text citations are used and provided on the slide or within the speaker notes.· Slides, speaker notes, and references are consistent with APA 6th edition format.One deduction for each type of APA format error.
2–3 APA errors are present
APA guidelines, as per the 6th edition of the manual, are demonstrated for the following:· In-text citations are used and provided on the slide or within the speaker notes.· Slides, speaker notes, and references are consistent with APA 6th edition format.One deduction for each type of APA format error.
4–5 APA errors are present
APA guidelines, as per the 6th edition of the manual, are demonstrated for the following:· In-text citations are used and provided on the slide or within the speaker notes.· Slides, speaker notes, and references are consistent with APA 6th edition format.One deduction for each type of APA format error.
6–7 APA errors are present
APA guidelines, as per the 6th edition of the manual, are demonstrated for the following:· In-text citations are used and provided on the slide or within the speaker notes.· Slides, speaker notes, and references are consistent with APA 6th edition format.One deduction for each type of APA format error.
8 or greater APA errors are present
References and Slide Count Note: Students are to use at least three (3) scholarly references. The PowerPoint presentation must be 7 total slides (excluding title and reference slides).Chamberlain NR501 Jean Watsons Theory of Human Caring Presentation3 Point deduction Does not use at least three (3)scholarly references and/or does not meet or exceeds required number of slides.Presentation of Slides5 Points4 Points 2 Points0 PointsPowerPoint presentation addresses all of the following elements:· Title slide· Reference slide(s)· Slides are professional in appearance and tone.
· Slides are balanced spatially, including words and graphics.
· Color is effective.
PowerPoint presentation does not address on or two of the following elements:· Title slide· Reference slide(s)· Slides are professional in appearance and tone.
· Slides are balanced spatially, including words and graphics.
· Color is effective.
PowerPoint presentation does not address three of the following elements:· Title slide· Reference slide(s)
· Slides are professional in appearance and tone.
· Slides are balanced spatially, including words and graphics.
· Color is effective.
PowerPoint does not address four or more of the following elements:· Title slide· Reference slide(s)
· Slides are professional in appearance and tone.
· Slides are balanced spatially, including words and graphics.
· Color is effective.
Writing Mechanics5 Points4 Points3 Points2 Points0 Points1–2 errors or exceptions to the rules of grammar, spelling, word usage, punctuation, and other aspects of formal written work as found in the 6th edition of the APA manual3–4 errors or exceptions to the rules of grammar, spelling, word usage, punctuation, and other aspects of formal written work as found in the 6th edition of the APA manual5–6 errors or exceptions to the rules of grammar, spelling, word usage, punctuation, and other aspects of formal written work as found in the 6th edition of the APA manual7–8 errors or exceptions to the rules of grammar, spelling, word usage, punctuation, and other aspects of formal written work as found in the 6th edition of the APA manual9 or greater errors or exceptions to the rules of grammar, spelling, word usage, punctuation, and other aspects of formal written work as found in the 6th edition of the APA manualFormat Subtotal ____/ 15pointsTotal Points ____/100pointsComments:Purpose
Master’s prepared nurses actively engage in the process of translating nursing knowledge into practice, thereby establishing evidence-based approaches within the discipline. Throughout this process, a theoretical framework provides a meaningful context to guide and support the evidence-based practice. The purpose of this assignment is to identify a theory or model which can be used as a framework for a future evidence-based project within the MSN program.
Course Outcomes
Through this assessment, the student will meet the following Course Outcomes:
- Apply nursing theory as a framework to guide the translation of knowledge and implementation of evidence-based practice in future professional settings.
- Analyze theories from nursing and relevant fields with respect to the components, relationships among the components, and application to advanced nursing practice.
Select a theory or model (Let’s select, The Jean Watson Theory-Caring) which is relevant to your selected area of advanced practice nursing (Family nurse practitioner-my selected area of advanced practice) and would offer a meaningful context for evidence-based practice surrounding the issue or concern which you identified (Palliative care).
In a PowerPoint Presentation, address the following.
- Introduction to the presentation.
- Identify and describe a theory or model, and explain its relevance to the selected area of advanced practice
- Describe an issue or concern regarding the selected area of advanced practice, and explain its impact on health care outcomes
- Explain how the theory or model can be used as a framework to guide evidence-based practice to address the issue or concern, and discuss the unique insight or perspective offered through the application of this theory or model.
- Conclusion to the presentation
- References
Submission Requirements
Application: Use Microsoft Word 2013™ to create the PowerPoint presentation.
- Length: The PowerPoint presentation must be 7 total slides (excluding title and reference slides).
- Speaker notes are used and include in-text citations when applicable.
- A minimum of three (3) scholarly literature sources must be used.
Jean Watson Theory of Human Caring and Nursing Informatics Sample Paper
Jean Watson Theory of human caring was developed between 1975 and 1979 and has since been embraced as the basis of nursing practice (Durgun Ozan & Okumu?, 2017). Durgun Ozan and Okumu? (2017) further illustrate the theory’s aim as moving away from treatment centeredness to caring. Nursing informatics on the other hand is a major component of modern healthcare that incorporates clinical and technical languages of health and translates them into one (Collins et al., 2017). In this particular writing, an issue related to nursing and nursing informatics will be selected, discussed along with its resolution using Jean Watson’s theory of human caring.
Ethical Issues in Nursing and Nursing Informatics
Nursing informatics focuses on providing meaningful, user-friendly, and patient-centered innovation while spearheading better outcomes for patients and enhancing clinical workflow for healthcare staff (Iyengar et al., 2018). However, this field is faced with a lot of concerns as it tries to integrate care and technology.
One of the issues encountered is ethical issues. Ethical issues in nursing and nursing informatics gamut from failing to log off the computer after use, illegally accessing patient records, lending access codes, not shredding private information, texting patient information to losing electronic devices (Wilburn, 2018). Teoli and Ghassemzadeh (2020) stress that the transformation of healthcare ecosystems has led to the growing concern of privacy of patients and healthcare providers regarding health informatics.
Relevance of Jean Watson Theory of Human Caring to Nursing Informatics
Jean Watson Theory as well as nursing informatics aims at improved patient care. The theory insists that nurses practice a holistic caring approach. To create this healing environment the caregivers themselves have to recover and then focus on the 10 carative factors (Kathleen, 2017). Evolution of the nursing informatics is based upon the tenth carative factor- open to mystery. This phrase encouraged nurses to be innovative, creative, and explore the unknown to become more knowledgeable.
Consequently, several advancements including electronic health records have been developed (Kathleen, 2017). Similarly, the emergency of the digital age has increased nursing interactions with resultant transdisciplinary, multicultural and global caring (Kathleen, 2017). Additionally, Collins et al. (2017) in their study found out that 74 out of 118 nursing informatics competencies were acquired through job training.
Resolution of Ethical Issues in Informatics Using Jean Watson Theory
The 10 carative factors accentuated by Watson’s Theory of human caring can be used to solve ethical issues in nursing and nursing informatics. For example, a nurse that has developed a helping-trust relationship cannot text confidential patient information or allow unauthorized access to this sensitive information. Also, a healthcare provider with a formed humanistic-altruistic system of values won’t access patient records illegally. At the same time, the theory also proposes that caregivers have to watch themselves out and this will likely reduce the instances of lending access codes and failing to log off computers after use. It is crystal clear that ethical issues in informatics can be resolved if nurses fully embrace Jean Watson’s Theory of human caring.
My philosophy of nursing which is to offer patient-centered evidence-based and holistic nursing care connects to Watson’s Theory of Human caring which also highlights caring as key to all nurses. My practice as a nurse is intertwined within the theory and am always motivated and/or satisfied when patient interests are prioritized as well as rationalizing every intervention.
These together with my professional code of conduct allows me to take care of the privacy of patient’s information along with other ethical issues in nursing and nursing informatics. McCutcheon and Stalter (2017) in the article “Discovering My Nursing Philosophy” realize that nursing is an art because it transcends the physical dimension. As a surgical nurse involved in perioperative care and from his experience urges that nursing care should be patient-focused with compassion and flexibility concerning the dynamic nursing philosophy.
Conclusion
The crucial role of Jean Watson Theory of Human Caring in nursing practice cannot be overemphasized. In the nursing and nursing informatics, the principles and the carative factors of the theory can help solve some of the issues in this fascinating field. Ethical issues and considerations are key to the practice of all professionals and need to be dealt with. Each nurse should develop a nursing philosophy although patient centered care is indispensable.
References
- Collins, S., Yen, P.-Y., Phillips, A., & Kennedy, M. K. (2017). Nursing informatics competency assessment for the nurse leader: The Delphi study: The Delphi study. The Journal of Nursing Administration, 47(4), 212–218. https://doi.org/10.1097/NNA.0000000000000467
- Durgun Ozan, Y., & Okumu?, H. (2017). Effects of nursing care based on Watson’s theory of Human Caring on anxiety, distress, and coping, when infertility treatment fails: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Caring Sciences, 6(2), 95–109. https://doi.org/10.15171/jcs.2017.010
- Iyengar, A., Kundu, A., & Pallis, G. (2018). Healthcare Informatics and Privacy. IEEE Internet Computing, 22(2), 29–31. https://doi.org/10.1109/mic.2018.022021660
- Kathleen, S. (2017). Evolution of Watson’s human caring science in the digital age. International Journal for Human Caring, 21(1), 46–52. https://doi.org/10.20467/1091-5710.21.1.46
- McCutcheon, K. A., & Stalter, A. M. (2017). Discovering my nursing philosophy. Nursing, 47(5), 68–69. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NURSE.0000515502.72414.38
- Teoli, D., & Ghassemzadeh, S. (2020). Informatics Ethics. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538512/
- Wilburn, A. (2018). Nursing informatics: Ethical considerations for adopting electronic records. NASN School Nurse, 33(3), 150–153. https://doi.org/10.1177/19
READ MORE >>
